Figure 2.
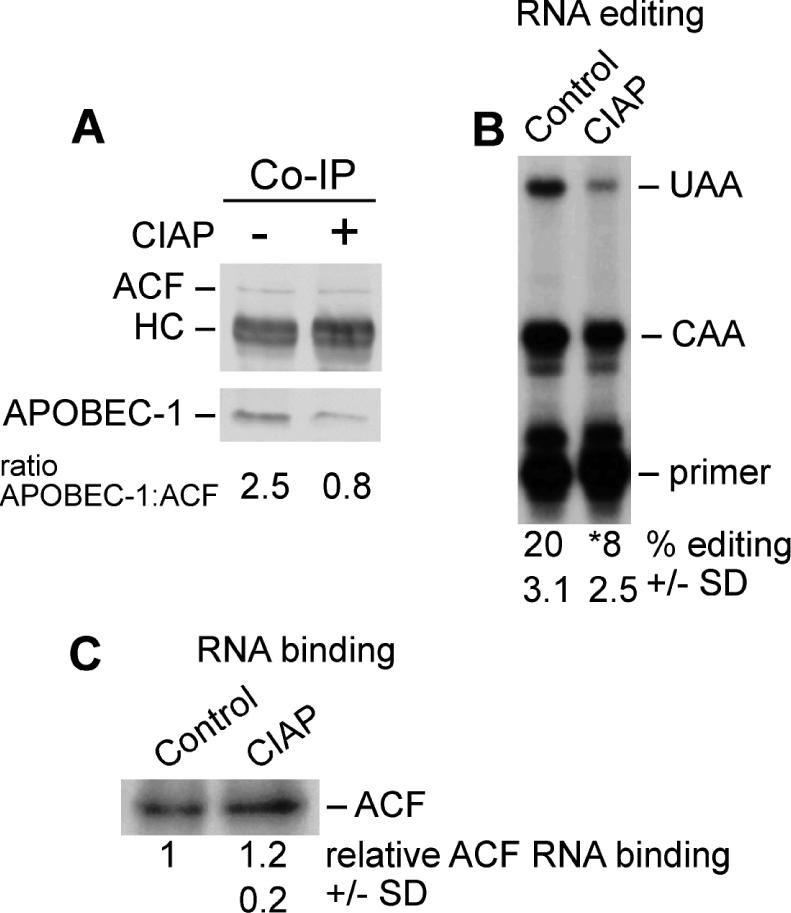
Phosphatase treatment inhibits apoB mRNA editing. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation: The HA-tagged APOBEC-1 overexpressing McArdle cell line was treated with ethanol for 4 h and fractionated. Nuclear extracts were immunoprecipitated with ACF CT antibody and processed as described in Figure 1. For CIAP treatment extracts were adjusted to 5 mM MgCl2, 3 mM CaCl2, 0.1 mM ZnCl2 and 25% glycerol and then incubated with 5 U CIAP for 1 h at 30°C. Control extracts were treated similarly but lacked phosphatase. The ratios of APOBEC-1:ACF were determined by scanning densitometry and quantitation using ImageJ Software. HC, position of Ig heavy chain. (n = 4, SD ±0.2). (B) In vitro editing activity: Liver nuclear extract was treated with CIAP as described above. In vitro editing activity was determined using the poisoned-primer extension assay. The percent editing was quantified by PhoshorImager (Molecular Dynamics) scanning densitometry. (n = 4, SD ± 0.2, p ≤ 0.01). (C) RNA binding: ACF RNA binding activity was determined by ultraviolet light induced cross-linking of liver nuclear extracts. Quantitation of relative amounts of ACF bound was performed using PhoshorImager scanning densitometry. (n = 4, SD ± 0.2, p ≤ 0.01).
