Summary
PubMed Informer is a Web-based monitoring tool for topics of interest from MEDLINE/PubMed primarily designed for healthcare professionals. Five tracking methods are available: Web access, e-mail, Short Message Service (SMS), PDA downloads and RSS feeds. PubMed Informer delivers focused search updates and specific information to users with varying information-seeking practices.
Introduction
My NCBI, a service from PubMed, features an option to automatically e-mail search results. The goal of PubMed Informer (PMI) [1] is to monitor updates for MEDLINE/PubMed searches then alert users through multiple methods. Aside from e-mail alerts, PMI integrates SMS for mobile phones, AvantGo channels for PDAs and RSS feeds, thereby providing more options for notification.
System Description
PMI is a Web-based system developed with Apache, MySQL and PHP. Scheduled PHP scripts send structured queries to Entrez Programming Utilities (eUtils) and retrieve an XML document with the results. A custom-made PHP class parses the XML elements. Parsed data is stored in the database and processed for different alert methods.
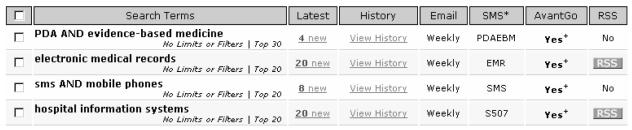
Users register and login through the PMI Web site. Search options can include limits, clinical study or systematic review filters. The Web site interface (see Figure 1) is designed for fast browsing with details available at a glance. Previous results are viewed through search histories. Archived articles for each search can be viewed online through the PMI Web site or offline through PDA downloads.
Figure 1.
PubMed Informer Web Interface
Users are notified through five alert methods:
Web site: Users can view the latest results for their topics, browse through the retrieved citations and read abstracts within the PMI Web site.
E-mail Alerts: E-mail is sent on a user-preferred schedule (daily, weekly, every 2 weeks or monthly) that may contain abstracts and links to PMI and PubMed of the retrieved results.
SMS Alerts: Text messages sent to mobile phones supplement e-mail alerts. Each search is assigned a specific SMS Term. SMS alerts activated within the PMI interface are sent simultaneously with e-mail alerts using an e-mail-to-SMS messaging service.
PDA Downloads: Handheld-friendly Web pages are generated for PDA browsers. The AvantGo [2] browser can be used to download pages for offline viewing. Abstracts are included in PDA downloads. Users update by synchronizing with their computers connected to the Internet. A unique channel id is provided for personal downloads.
RSS Feeds: PMI also generates an XML document compliant to RSS 2.0 standards. With RSS feeds, newest articles for topics of interest from MEDLINE/PubMed can be monitored through RSS-capable browsers, Web site feeds and desktop applications. PDA and RSS results are updated daily.
Conclusion
PubMed Informer integrates several communication technologies to inform users of the latest articles from MEDLINE/PubMed. Web access, e-mail, SMS on mobile phones, AvantGo channel to PDAs and RSS feed provide access to summaries of updated medical information. Evaluation studies to determine the effect on information-seeking behavior are underway.
References
- 1.PubMed Informer. http://pmi.nlm.nih.gov
- 2.AvantGo. http://www.avantgo.com