Figure 7.
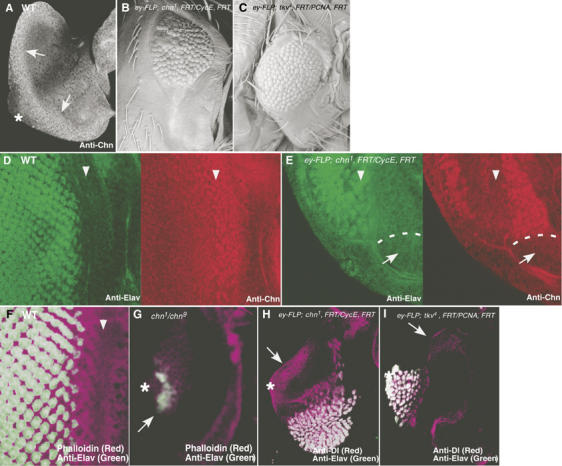
chn is required for eye morphogenesis. (A) In wild-type eye discs from early third instar larvae, Chn expression was detected at the posterior edge of the disc using anti-Chn antibody (arrows). (B, C) Adult eye morphology. (B) ey-FLP; chn1, FRT42D/PCNA775, FRT42D. Large clones of chn1 were formed and caused the small eye phenotype. (C) ey-FLP; tkv4, FRT40A/CycEAR95, FRT40A. A large clone of tkv4 showed a similar eye defect. (D) In wild-type eye disc, Elav (green) was expressed behind the MF (left panel), marked with Chn (red; right panel). (E) In eye discs with large clones of chn1, Elav-positive cells were greatly reduced in number (green; left panel, arrowheads) and were always associated with residual chn expression (red; right panel). White dots represent the border of chn1 clone (arrows). (F) Wild-type eye disc stained with phalloidin (purple) and anti-Elav (green). (G) chn1/chn9. Strong chn mutations eliminated the MF, whereas a few Elav-positive cells can be observed (arrow). (H) In eye discs with large clones of chn1, ectopic expression of Dl was detected at the posterior edge of the disc (arrow). (I) Large clone of tkv4 did not induce ectopic Dl expression (arrow). Asterisks represent the position of the optic stalk where the MF propagation initiates, and arrowheads represent the position of the MF.
