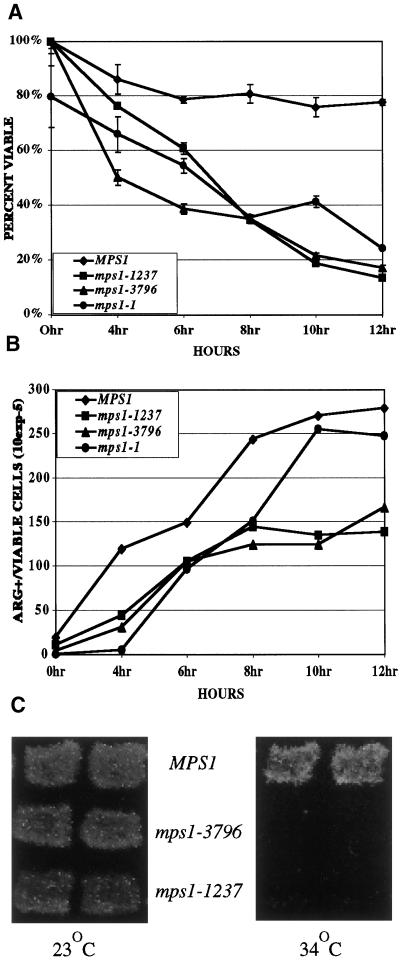
Figure 1.
Return-to-growth assays were done to determine viability (A) and commitment to recombination (B) with the use of wild-type (YUMY3E3), mps1-1 (YUMY131 × YUMY1D1), mps1-1237 (YUMY3I1), and mps1-3796 (YUMY3I8) homozygous diploid mutant strains. Strains were synchronously sporulated, and aliquots of cells were plated to SC or SC-arginine medium at the times indicated. Viability was measured as the number of CFU at each time point as a percentage of CFU at 0 h. Commitment to recombinationwas determined with the use of arg4 heteroallelic diploids and plating to SC-arginine medium. Recombinant frequency is expressed as Arg+ colonies per CFU at each time point according to the method described by Esposito and Esposito (1974). Recombination assays were performed three times with triplicate samples. One representative example is shown. (C) Viability of cells sporulated at the restrictive temperature was assessed with the use of Can/Cyh resistance generated by haploidization of two recessive drug-resistance markers. Wild-type (TM002), mps1-3796 (TM019), and mps1-1237 (TM027) strains were sporulated at room temperature and 34°C. Patches were replica plated to medium containing cycloheximide and l-canavanine (see MATERIALS AND METHODS) and incubated at room temperature for 2–5 d to assay viable haploid cell production caused by haploidization of both can1-100 and cyhr markers.