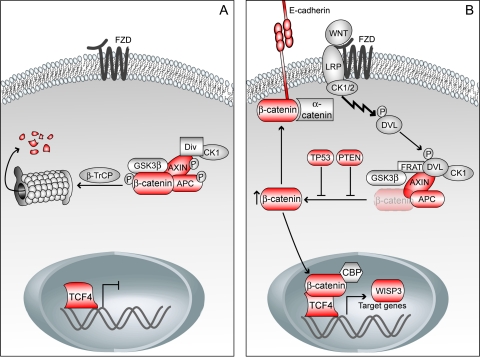
Figure 1.
(A) In the absence of a WNT signal, a multiprotein complex consisting of β-catenin, APC, AXIN, GSK-3β, diversin (Div), and CK1 is formed, leading to phosphorylation and subsequent proteosomal degradation of β-catenin. (B) In the presence of a WNT signal, the multiprotein complex is not formed properly and β-catenin remains unphosphorylated and accumulates in the cytoplasm. Free cytosolic β-catenin translocates into the nucleus, leading to transcription of downstream target genes. It might also form a complex with E-cadherin and α-catenin and participate in cell-cell adhesion. The tumor-suppressor proteins TP53 and PTEN indirectly inhibit activation of the WNT signaling pathway. Components with red color are investigated in the present study. β-TrCP, β-transducin repeat-containing protein; CBP, CREB-binding protein; DVL, dishevelled; FRAT, frequently rearranged in advanced T-cell lymphomas; FZD, frizzled; LRP, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein.