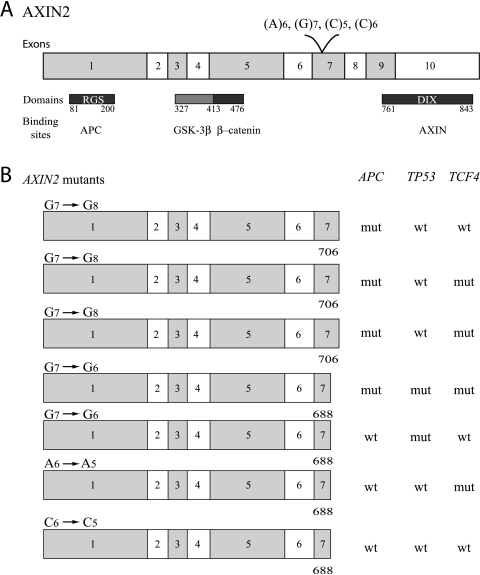
Figure 6.
(A) The coding region of AXIN2 and corresponding domains and binding sites. (B) The consequence of the different AXIN2 mutations in relation to mutations in APC, TP53, and TCF4. Insertion of one G in the (G)7 repeat of AXIN2 predicted stop at amino acid 706, whereas all the other mutations predicted stop at amino acid 688. In both situations, loss of the DIX domain was observed. Four tumors with AXIN2 mutations were concurrently mutated in APC.