Figure 4.
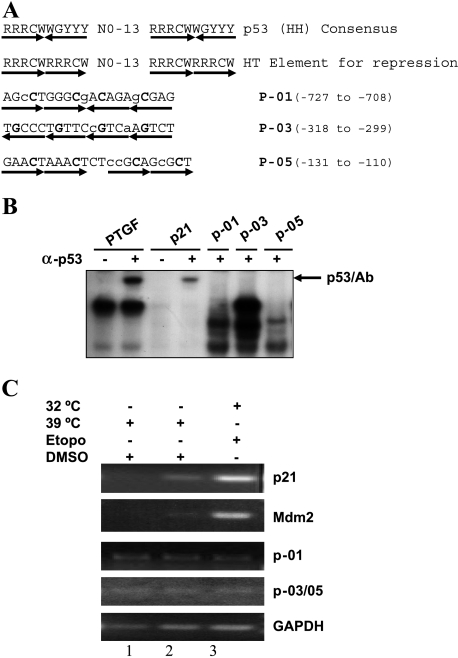
p53 failed to bind to three putative p53 binding sites in the SAK promoter. (A) Listed are the sequences of the p53 consensus binding site for activation (line 1) and repression (line 2) [23] and three putative p53 binding sites within the SAK promoter region (lines 3–5). R = purine, Y = pyrimidine, W = A/T, H = head, T = tail. The mismatches in SAK promoter sequences are indicated with lower case letters and the core sequences are indicated in bold face. (B) In vitro gel retardation assay. The assay was performed as detailed in the Materials and Methods section. The probe PTGF (5′-AGCCATGCCCGGGCAAGAAC-3′) and its complementary strand from the promoter of the PTGF-β gene [54], and p21 (5′-GAACATGTCCCAACATGTTG-3′) and its complementary strand from the promoter of p21 gene [11], were used as positive controls in the assay. p53/Ab indicates the supershifted complex in the presence of p53 antibody, pAb421. (C) In vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation. p21 and Mdm2 are used as positive controls, and GAPDH is used as a negative control. Since two putative p53 binding sites, P-03 and P-05, are adjacent to each other, only one pair of PCR primers was used to detect potential p53 binding to any one of them. Total cell extracts were prepared from H1299/Neo (lane 1) and H1299-V138 (lanes 2 and) cells treated with either DMSO or 25 µM etoposide for 24 hours at 39°C or 32°C. The assays were performed as detailed in the Materials and Methods section.