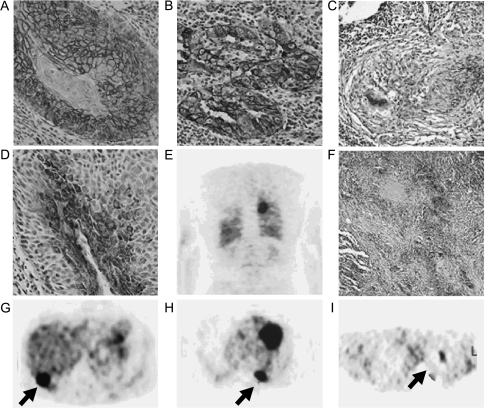
Figure 2.
Immunohistochemical findings and [18F]FDG-PET examinations from selected patients enrolled in the present study. (A, D, and G) Glut-1 expression, HK-II expression, and [18F]FDG-PET examination from the same patient (patient 33) with well-differentiated SCC, respectively. The highest expression of Glut-1 was observed in the membranes of cancer cells (grade 5) (original magnification, x 10), whereas the expression of HK-II was observed throughout the cytoplasm as small punctuate areas (grade 4) (original magnification, x 10). The [18F]FDG-PET examination showed a high [18F]FDG uptake in the posterior lower lobe of the right lung (panel G; arrow) on the transaxial slice (pSUV = 14.1). (B, E, and H) Glut-1 expression and two representative [18F]FDG-PET reconstructed slices (coronal and transaxial slices, respectively) from a patient (patient 21) with AC (papillary type, moderate differentiated), respectively. The expression of Glut-1 can be observed in the membranes of cancer cells and as granules throughout the cell cytoplasm (grade 5) (original magnification, x 10). The [18F]FDG PET examination showed a high uptake in the left lung (panel H; arrow) (pSUV = 12.4). (C, F, and I) Glut-1 expression, HK-II expression, and [18F]FDG PET examination from a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis (patient 48), respectively. The expression of Glut-1 can be observed in the membranes of cells in the center of the pulmonary granuloma (grade 2) (original magnification, x4), whereas the expression of HK-II can be observed in areas surround caseating granulomas throughout the cytoplasm (grade 3) (original magnification, x4). The [18F]FDG-PET examination showed a moderate [18F]FDG uptake in the upper lobe of the left lung (panel I; arrow) on the transaxial slice (pSUV = 6.9).