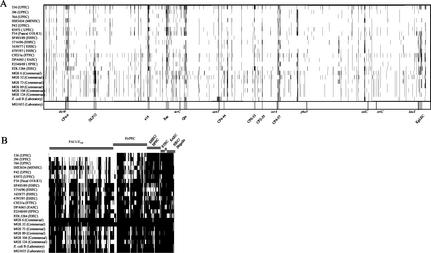
FIG. 2.
Detection of genomic alterations among pathogenic, commensal, and laboratory E. coli strains using DNA arrays. (A) Comparison of genomes of different pathogenic, commensal, and laboratory E. coli isolates and the E. coli K-12 strain MG1655 using Panorama E. coli gene arrays. The individual chromosomes are displayed linearly and in equal lengths. Missing-undetectable ORFs are marked by vertical black lines in the individual chromosomes. The positions of the undetectable ORFs refer to the E. coli MG1655 chromosome. The positions of tRNA genes frequently used as chromosomal insertion sites of horizontally acquired DNA elements and those of 10 prophages of strain MG1655, as well as the chromosomal origin and terminus of replication, are marked within the map of E. coli strain MG1655. (B) Detection of virulence-associated genes of E. coli and Shigella among pathogenic and commensal E. coli isolates using the E. coli pathoarray. Virulence-associated genes are grouped with regard to typical E. coli pathotypes. Missing-undetectable ORFs are marked by vertical black lines.