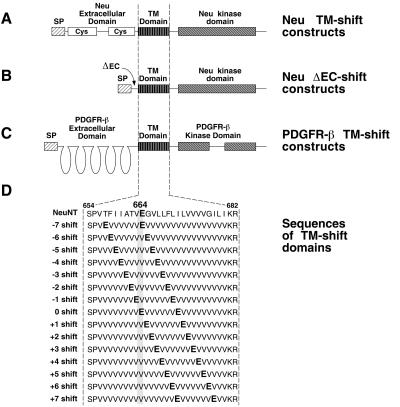
Figure 1.
Structure of the TM-shift mutants. (A) Neu TM-shift constructs containing simplified transmembrane domains with a dimerization motif. (B) Neu ΔEC-shift constructs containing simplified transmembrane domains with a dimerization motif. In these constructs, nearly the entire extracellular domain (amino acids 30–628) was deleted (ΔEC). (C) PDGFR-β constructs containing TM-shift domains with a dimerization motif. (D) The amino acid sequence is shown for each of the 15 transmembrane domains of the TM-shift mutants. The cysteine-rich regions (Cys) of the extracellular domain of Neu are shown. All constructs contain a signal peptide (SP) for membrane translocation and a mutated transmembrane (TM) domain that replaces residues 654–682 of Neu and residues 499–527 of murine PDGFR-β.