Figure 3.
Seeds from a [fie-1/FIE × FIE/FIE; METI a/s/METI a/s] Cross.
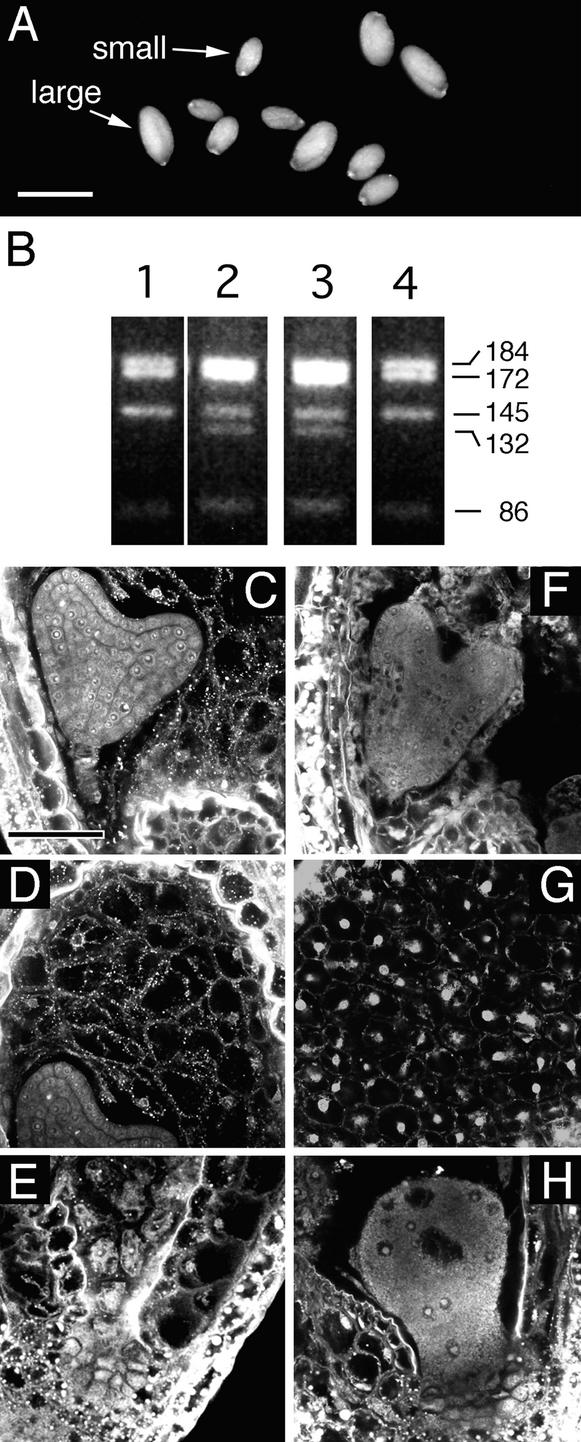
(A) Light microscopy image showing the two classes of seeds. All seeds are plump, indicating that a pollen parent hypomethylated by the METI a/s transgene can rescue fie-1 mutant seeds.
(B) Identification of the fie-1 and FIE alleles by PCR and restriction enzyme analysis (see Methods). The wild-type FIE allele produces four bands (lane 1), whereas fie-1/FIE heterozygotes (lane 2) have an extra band. All large seeds scored had the heterozygous pattern (lane 3), whereas all small seeds were wild type (lane 4).
(C) to (H) Confocal microscopy images of seeds at 8 DAP. The seed in (C) to (E) has a phenotype similar to seeds from interploidy crosses generating maternal genomic excess, whereas the seed in (F) to (H) shows characteristics of paternal excess (see text; Scott et al., 1998).
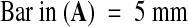 ;
; 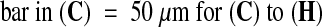 .
.