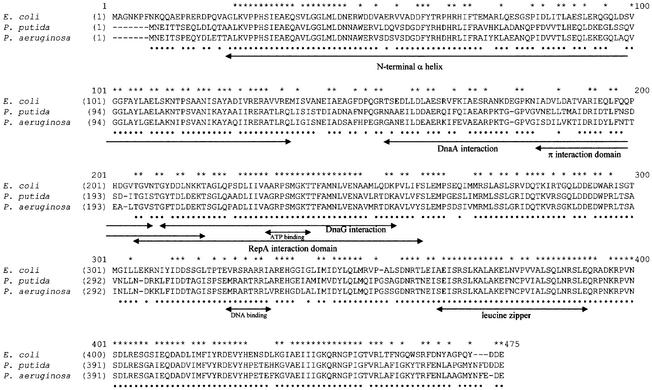
Fig. 1. Sequence alignment of DnaB proteins from different bacteria. Alignment of the E.coli DnaB protein with the replicative helicases of P.putida and P.aeruginosa was performed using ClustalX. Regions of the E.coli DnaB protein that have been identified or implicated in interactions with other proteins are indicated by arrows: N-terminal α-helix domain (Miles et al., 1997); DNA-binding and leucine zipper (Biswas et al., 1994; Biswas and Biswas, 1999); DnaA interaction (Seitz et al., 2000); DnaG interaction (Lu et al., 1996); and plasmid-encoded Rep protein interaction (R6K π and pSC101 RepA) (Ratnakar et al., 1996; Datta et al., 1999). An asterisk above the alignment indicates residues that are identical in all three proteins; a dot below the alignment indicates residues that are identical between the two Pseudomonas species only. On the basis of the predicted amino acid sequences, the molecular weight of each of the two Pseudomonas DnaB proteins is 59.6 kDa.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.