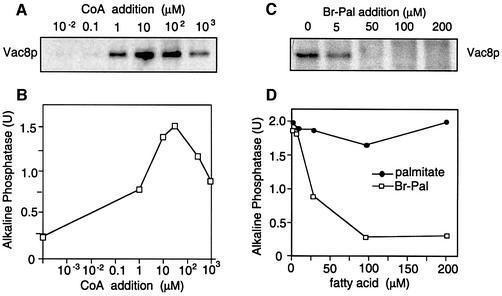
Fig. 2. Requirements for Vac8p palmitoylation and vacuole fusion coincide. (A) Vac8p palmitoylation requires an optimal CoA concentration. A fusion reaction (300 µl) containing 60 µg of vacuoles from DKY6281 was incubated for 60 min in the presence of cytosol, ATP, [3H]palmitate and increasing amounts of CoA. Palmitoylated Vac8p was identified by SDS–PAGE and fluorography as described in Figure 1. (B) Vacuoles from both tester strains were incubated in a 30 µl reaction volume under similar conditions with varying CoA concentrations to determine fusion activity. (C) Addition of Br-Pal blocks Vac8p palmitoylation. Vacuoles (60 µg) were incubated in a 300 µl volume for 60 min in the presence of ATP, cytosol, CoA and [3H]palmitate. Br-Pal was added at the indicated concentrations to the fusion reaction. Palmitoylated Vac8p was analyzed as in (A). (D) Fusion is blocked by Br-Pal. Vacuoles from both tester strains were incubated at 26°C in the presence of ATP, CoA, cytosol and Br-Pal or palmitate at the indicated concentrations. Fusion was determined after 90 min incubation. Note that palmitate has no stimulatory effect on vacuole fusion if cytosol is added to the assay (see also lanes 8 and 10 in Figure 1A).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.