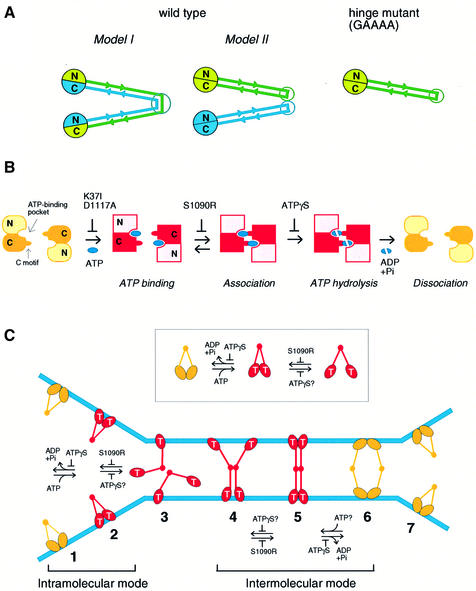
Fig. 7. Models. (A) Configuration of BsSMC. In wild-type BsSMC, dimerization may be mediated by coiled-coil interactions between two different subunits (Model I). Alternatively, the two subunits are self-folded to form two separate coiled-coil rods, which in turn dimerize by a hinge-mediated interaction (Model II). The GAAAA mutant is likely to be a self-folded monomer (right), and no alternative can be considered for the folding of this mutant. (B) ATP binding and hydrolysis cycle of BsSMC. Putative arrangement of the ATP binding pocket and the C motif is drawn on the basis of the crystal structure of the Rad50 catalytic domain (Hopfner et al., 2000). N and C indicate the N- and C-terminal domains of BsSMC, respectively. (C) Bimodal activation of SMC ATPase. The ATP-bound form of end domains is indicated by T. Each stage of conformational changes of BsSMC on DNA is numbered from 1 to 7. See the text for details.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.