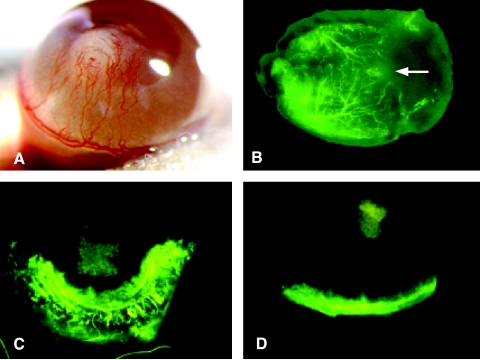
Figure 6.
SB-HSA cells are potent inducers of angiogenesis and IL-12 inhibits this effect. (A) A polyvinyl sponge containing 70,000 SB-HSA cells was placed into a surgically created corneal pocket in a BALB/c mouse. After 12 days, a robust angiogenic response is visible in the cornea, with neovascularization arising from the limbus and proceeding toward the sponge implant (white structure in the center of the cornea). Implanted sponges that did contain SB-HSA cells failed to provoke an angiogenic response. Experiment shown is representative of eight mice, all exhibiting a similar response. (B) Matrigel, an artificial connective tissue matrix, was injected subcutaneously in the flank of a BALB/c mouse. After solidifying, a nick was made into the Matrigel through a skin incision, and a polyvinyl sponge (arrow) containing 5 x 106 SB-HSA cells was inserted into the Matrigel. After 2 weeks and 3 to 5 minutes prior to sacrifice, 200 µl of FITC-dextran was injected into the tail vein and the Matrigel plug was removed. Under fluorescence microscopy, a pronounced angiogenic response was observed (arborized fluorescent green vessels), which progressed toward the proliferating SB-HSA cells in the sponge. These experiments confirm the proangiogenic properties of SB-HSA cells. The effect of IL-12 on SB-HSA-induced corneal angiogenesis was compared in BALB/c control mice given PBS (C) by continuous subcutaneous infusion versus BALB/c that received 1 µg/day mrIL-12 for 7 days by continuous subcutaneous infusion (D). Mice treated with IL-12 had significantly less corneal neovascularization compared to the control mice (P < .05). Mice were injected with FITC-dextran just prior to euthanasia and corneal vessels were evaluated with fluorescence microscopy. In this example, there was a 56% reduction in corneal neovascularization in the IL-12-treated mouse. The fluorescent vessel in the ventral aspect of the cornea in (D) is the normal limbic vessel and the green squares in the centers of (C) and (D) are the SB-HSA sponges that have absorbed fluorescein. Note that vessels have nearly reached the sponge in (C) whereas the cornea in (D) remains relatively avascular.