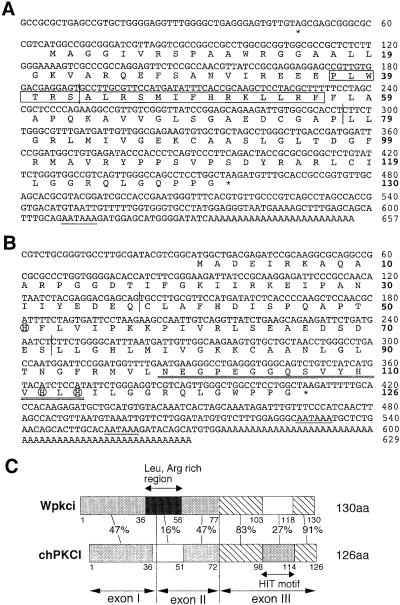
Figure 1.
The cDNA and deduced amino acid sequences of Wpkci (A) and chPKCI (B) and comparison of the levels of sequence identity of their protein subregions (C). The cDNA sequences of pWpkci-8 (A) and pchPKCI-3 (B) were determined. The N-terminal Met residue in A was assigned because of its location nearest to the termination codon in the 5′ untranslated region, and that in B was assigned by comparison with the mammalian PKCI sequences. In A and B, termination codons (asterisks), polyadenylation signals (underlines), and boundaries of exons (vertical lines) are indicated. The Leu- and Arg-rich region of Wpkci is boxed in A. The HIT motif containing the conserved His triad (HVHLH) is double-underlined, and the three His residues involved in the binding of zinc are circled in B. In C, the residue numbers for the N terminus, the C terminus, and the last residue of each region, correspondence to exons I–III, and levels (%) of identity of the deduced sequences between corresponding regions of Wpkci and chPKCI are indicated. The sequences of the inserts of pWpkci-8 and pchPKCI-3 are deposited in the DDBJ, EMBL, and GenBank nucleotide sequence databases with accession numbers AB026677 and AB026675, respectively.