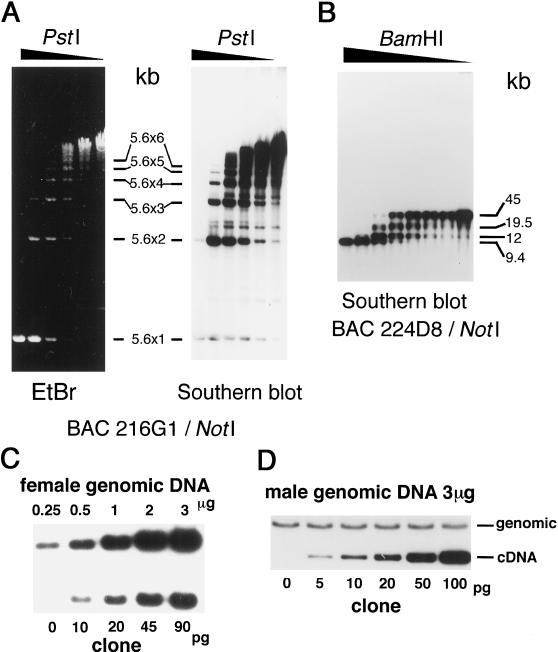
Figure 4.
Determination of reiteration frequencies of Wpkci and chPKCI in the chicken genome. (A) The 140-kb insert containing Wpkci genes was obtained from the BAC clone 216G1 by digestion with NotI and further digested with PstI at six different concentrations. The digests were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, stained with ethidium bromide (left panel), and subjected to Southern blot hybridization with the 32P-labeled insert of the cDNA clone fst5.2-5 (right panel; see Figure 2A), which showed signals corresponding to multiples of the 5.6-kb repeating unit. (B) The insert of BAC clone 224D8 containing the chPKCI gene sequence was obtained by NotI digestion, further digested with BamHI at eight different concentrations, and subjected to Southern blot hybridization with the 32P-labeled cDNA fragment (nucleotide positions 30–410) of chPKCI. (C) Different amounts of EcoRV-digested genomic DNA of the female chicken (upper panel) and EcoRV-digested genomic DNA of the male chicken (3 μg each) mixed with different amounts of the linearized cDNA clone p5fm2 (3.83 kb) (lower panel; see also Figure 2A) were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis and Southern blot hybridization with the 32P-labeled insert of p5fm2. Comparing the slopes of signal intensities for the former and the latter samples, 1 μg of the female genomic DNA and 72 pg of p5fm2 gave the same signal intensity. (D) The BamHI-digested genomic DNA of the male chicken (3 μg each) and different amounts of the HindIII-digested, linearized cDNA clone pchPKCI-3 were subjected to electrophoresis and Southern blot hybridization with the 32P-labeled subfragment (nucleotide positions 30–410) of pchPKCI-3. Comparing the mean signal intensity of the former and the slope of signal intensities of the latter samples, 3 μg of the male genomic DNA and 12 pg of pchPKCI gave the same signal intensity.