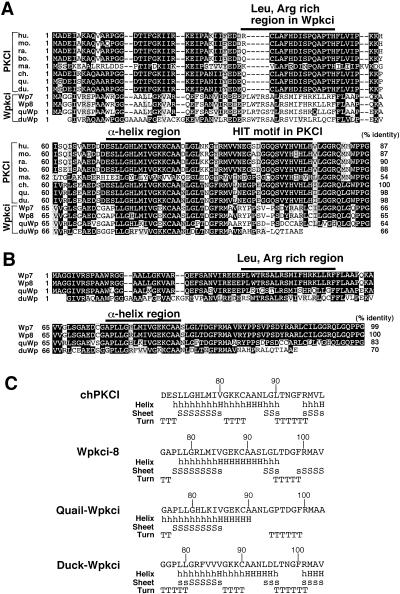
Figure 6.
Comparison of deduced amino acid sequences of mammalian, plant, and avian PKCI and avian Wpkci, and prediction of the α-helix for the fourth region of avian PKCI and Wpkci. (A) Deduced sequences of PKCI from human (hu.), mouse (mo.), rabbit (ra.), bovine (bo.), maize (ma.), chicken (ch.), Japanese quail (qu.), and domestic duck (du.) and of Wpkci from chicken (Wp7 and Wp8), Japanese quail, and domestic duck, abbreviated as above, were aligned, and three characteristic regions or a motif are indicated. Identical residues are shown with white letters on a black background and similar residues are shown on a stippled background. The overall level (%) of identity relative to the sequence of chicken PKCI is indicated at the end of each deduced sequence. Only a single residue is different between Wpkci-7 (Wp7) (H-81, minor type) and Wpkci-8 (Wp8) (R-81, major type) of chicken. (B) Alignment and comparison of the deduced sequences of Wpkci from chicken (Wp7 and Wp8), Japanese quail (qu), and domestic duck (du). Wpkci of domestic duck lacks the last 14 residues. (C) Prediction of α-helix (H or h) formation for the fourth region (see Figure 1C) of chPKCI and Wpkci of chicken (Wpkci-8), Japanese quail, and domestic duck. The cDNA sequences for Japanese quail PKCI (AB033882), domestic duck PKCI (AB033884), Wpkci-7 (AB033880), Japanese quail Wpkci (AB033881), and domestic duck Wpkci (AB033883) are deposited in the DDBJ, EMBL, and GenBank nucleotide sequence databases with the accession numbers shown in parentheses.