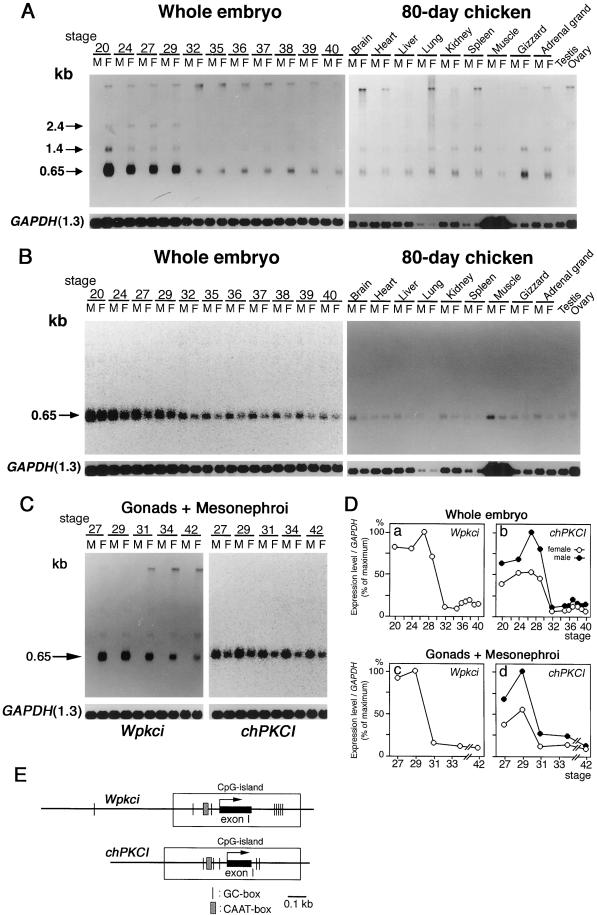
Figure 7.
Transcripts of both Wpkci and chPKCI genes are present at higher levels in early embryonic stages. (A and B) Poly(A)+ RNA preparations from 3- to 14.5-d (stages 20–40) male (M) and female (F) chicken whole embryos or from different tissues of 80-d chickens, as indicated, were subjected to Northern blot hybridization with the 32P-labeled cDNA probe specific for Wpkci (63-bp probe) (A) or chPKCI (72-bp probe) (B) and with 32P-labeled GAPDH cDNA probe (A and B), followed by autoradiography (A and the right panel of B for the 80-d chicken) or fluorescence image analysis (the left panel of B for the whole embryo). (C) Poly(A)+ RNA preparations from undifferentiated gonads plus mesonephroi of 5- to 16-d (stages 27–42) male (M) or female (F) chicken embryos, as indicated, were subjected to Northern blot hybridization with the 32P-labeled Wpkci-specific, chPKCI-specific, or GAPDH cDNA probe, followed by autoradiography (the left panel for Wpkci) or fluorescence image analysis (the right panel for chPKCI). (D) Relative values of the signal intensity of Wpkci mRNA or chPKCI mRNA to GAPDH mRNA, determined from the same Northern blot analyses, were plotted for female (○) and male (●) embryos at different stages. (E) Some common transcriptional elements around exon I of Wpkci and chPKCI predicted from the genomic sequences determined for pGP-3 and pGH3.3-3 (see Figure 2).