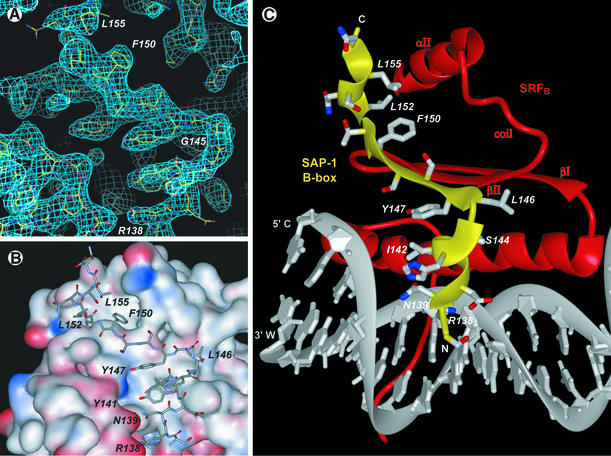
Fig. 4. Structure of the SAP-1 B-box sequence element bound to SRF. (A) Model of the SAP-1 B-box superimposed in the experimental electron density. The 2Fo – Fc electron density map calculated at 3.15 Å resolution is contoured at 1.5σ. The amino acid F150 is labeled to indicate the B-box polypeptide chain. The density at the lower left corresponds to DNA and at the upper right to SRF. (B) SAP-1 polypeptide chain bound to SRF shown as an electrostatic potential surface (red negative and blue positive charge). With the exception of the interactions with the DNA phosphate groups, the interaction surface is predominantly hydrophobic. The three aromatic amino acids Y141, Y147 and F150 contribute substantially to the SAP-1–SRF interaction interface, and the analogous amino acids in Elk-1 were identified as the most important for its addition to the ternary complex (Ling et al., 1997). (C) Side chains of the SAP-1 B-box stabilizing its bound conformation. R138 and N139 make hydrogen bonds to DNA phosphate groups. Y141, I142 and Y147 make a hydrophobic cluster by which the 3103 helix and β-strand interact. L146 extends along the surface of SRF, and F150 protrudes into the hydrophobic cleft formed by the SRF βII strand, coil region and αII helix. L152 and L155 bind the 3104 helix to SRF.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.