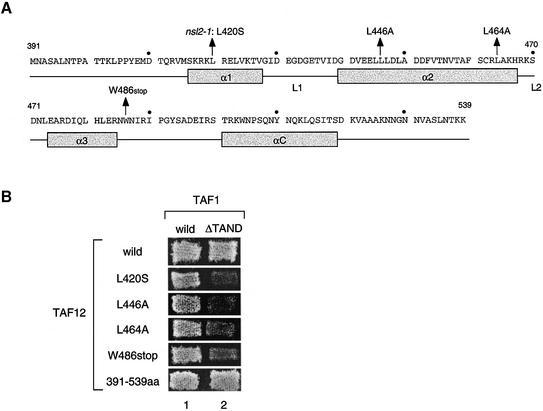
Figure 1.
Positions of nsl2/taf12 mutations and their nsl phenotypes. (A) Schematic representation of primary sequence and proposed secondary structures of the HFD of the TAF12 protein (53). Four α-helices are depicted as grey boxes and two linker regions between α-helices 1 and 2 or 2 and 3 are represented as L1 and L2 (53). The positions of the nsl2/taf12 mutations tested in this study are indicated with arrows above the primary sequence. The 410, 430, 450, 470, 490, 510 and 530 amino acids are marked with a dot. (B) The nsl phenotypes are shown by several nsl2/taf12 mutants. The LEU2-marked plasmid encoding either the wild-type TAF1 gene or the taf1-ΔTAND gene, as indicated at the top, was individually introduced into the strains with double deletions of TAF1 and TAF12 genes containing the TRP1-marked plasmid encoding each TAF12 derivative, as indicated on the left, in addition to the URA3 marked plasmid encoding wild-type TAF1. The resulting transformants were grown on 5FOA plates at 30°C for 5 days.