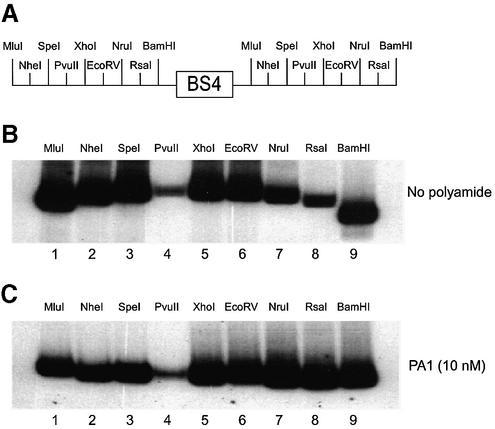
Figure 6.
A circular permutation assay was utilized to determine the effect of tandem hairpin PA1 on the intrinsic bend of a probe encoding the E2-DNA binding site. In this variation on an EMSA, a DNA fragment with a centralized bend will result in a lower mobility fragment whereas a DNA with a terminally positioned bend will result in a higher mobility fragment (57). (A) A schematic showing the relative positions of the tandemly duplicated restriction sites found on the radiolabeled probe encoding the BS4 E2-DNA binding site. (B) A circular permutation assay showing the radiolabeled probe restricted with the following enzymes: MluI (lane 1), NheI (lane 2), SpeI (lane 3), PvuII (lane 4), XhoI (lane 5), EcoRV (lane 6), NruI (lane 7), RsaI (lane 8) and BamHI (lane 9). (C) The circular permutation assay described in (B) is supplemented with 10 nM tandem hairpin polyamide PA1.