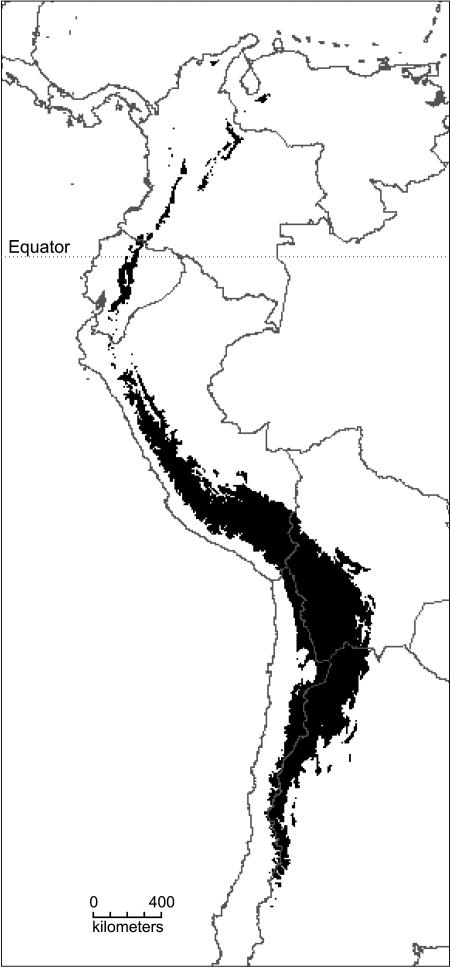
Fig. 1.
The Andes as an island archipelago. This map shows the distribution of land over 3,000 m elevation, corresponding to the lower limit of the high-altitude grassland (páramo, jalca, and puna) vegetation zone. Although a few Andean Lupinus species occur at lower elevations, the genus is most diverse in the 3,000- to 4,000-m zone. Lupinus species are ubiquitous in all of the high-elevation “islands” from Venezuela and the Sierra Nevada Santa Marta in northern Colombia in the north to northwest Argentina in the south, and the geographical extent of the Andean Lupinus radiation (Fig. 3, k) closely matches the overall area of the Andean “archipelago” as delimited here.