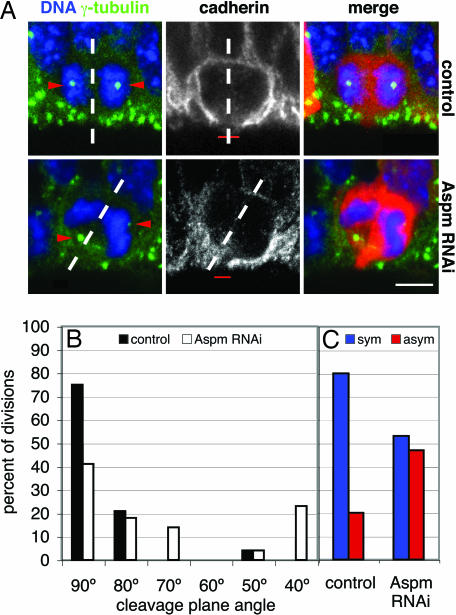
Fig. 3.
Knockdown of Aspm alters the cleavage plane of NE cells, resulting in their asymmetric division. (A) Cleavage plane and cadherin hole analysis. Mouse E12.5 dorsal telencephalon was either electroporated with mRFP plasmid only (Upper) or coelectroporated with Aspm esiRNAs and mRFP plasmid (Lower), followed by 24 h of in utero development, and cryosections were analyzed for NE cells in anaphase or telophase by DNA staining with DAPI (blue), RFP fluorescence (red), and γ-tubulin (green) and cadherin (white) immunofluorescence. The cleavage plane (dashed lines) was deduced from the orientation of the sister chromatids (5, 6). Note the aberrant position of the γ-tubulin-stained centrosomes (arrowheads, stack of optical sections) in the targeted cell and the oblique cleavage plane, which bypasses the cadherin hole (red bar, single optical section), upon Aspm knockdown. The apical surface of the VZ is down. (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (B and C) Quantification of cleavage plane orientation (B) and cadherin hole distribution (C). Dorsal telencephalon of E10.5 Tis21–GFP knockin mice was electroporated with mRFP plasmid only (control) or coelectroporated with mRFP plasmid and Aspm esiRNAs (Aspm RNAi), followed by 24 h of whole-embryo culture. Tis21–GFP-negative, mRFP-expressing NE cells in anaphase or telophase were analyzed for cleavage plane orientation and the position of the cadherin hole as in A. (B) Orientation of the cleavage plane relative to the radial, apical–basal axis of the neuroepithelium (defined as 90°), expressed as a percentage of all divisions for the control (black bars; n = 24) or Aspm RNAi (white bars; n = 22) condition. Groups of cleavage plane angle are ±5°. (C) Cleavage planes bisecting [symmetric (sym), blue bars] or bypassing [asymmetric (asym), red bars] the cadherin hole, expressed as a percentage of all divisions for the control (n = 15) or Aspm RNAi (n = 15) condition.