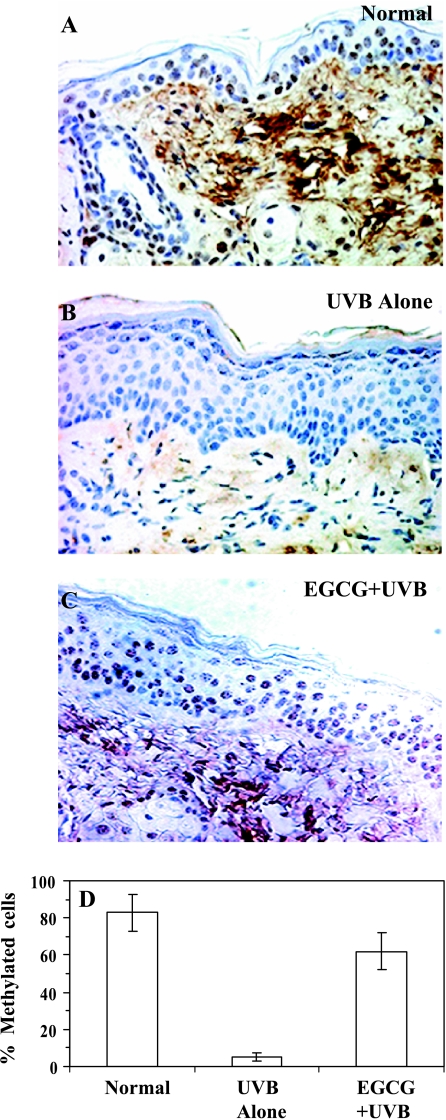
Figure 4.
Topical treatment of EGCG in hydrophilic cream inhibits UVB-induced global DNA hypomethylation pattern in chronically UVB-exposed mouse skin for 30 weeks. Immunohistochemical detection of DNA methylation pattern was performed using anti-5-mc monoclonal antibody as detailed in Materials and Methods section. Panel A: Normal skin (non-UVBexposed). Panel B: UVB irradiation alone. Panel C: EGCG + UVB-irradiated skin. Skin biopsies were subjected to staining for DNA methylation using antibody specific to 5-mc. Cells positive for 5-mc staining appears brown in color. Normal skin showed the presence of numerous positive cells in the epidermis (Panel A) whereas chronic exposure of UVB radiation induced global DNA hypomethylation pattern in the skin (Panel B). Pretreatment with EGCG prevented chronic UVB irradiation-induced global DNA hypomethylation in the skin (Panel C). Magnification, x 40. Panel D: The percentage of cells positive for 5-mc in the epidermis was plotted against different treatment groups as mean ± SD from four animals in each group.