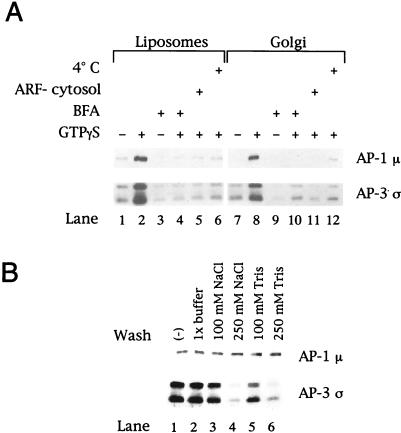
Figure 1.
AP-3 membrane recruitment is nucleotide, ARF, and temperature dependent and sensitive to brefeldin A. (A) Liposomes (200 μg/ml) prepared from soybean 20% PC material (lanes 1–6) or AP-1– and ARF-depleted Golgi-enriched membranes (50 μg/ml; lanes 7–12) were incubated in the presence or absence of 100 μM GTPγS in 200-μl reactions containing either 5 mg/ml gel-filtered bovine adrenal cytosol or 5 mg/ml bovine adrenal cytosol that had been depleted of ARF proteins by gel filtration over a Sephadex G-75 column (lanes 5 and 11). In reactions containing brefeldin A (BFA; lanes 3, 4, 9, and 10), a final concentration of 100 μg/ml BFA was used. After incubation at either 37 or 4°C (lanes 6 and 12) for 20 min, membranes were collected by centrifugation at 20,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C, fractionated on 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels, and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Portions of the blot were probed with affinity-purified antibodies directed against the μ subunit of AP-1 (antibody RY-1) or specific for the ς3A and ς3B isoforms of the AP-3 complex (Dell'Angelica et al., 1997a). (B) After recruitment of AP-1 and AP-3, the liposomal membranes were resuspended in 1× assay buffer or assay buffer containing 100 or 250 mM NaCl or 100 or 250 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0. After incubation on ice for 10 min, the membranes were recovered by centrifugation and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting as described in A. Shown are results with the liposomes. Similar findings were noted with the Golgi-enriched membranes.