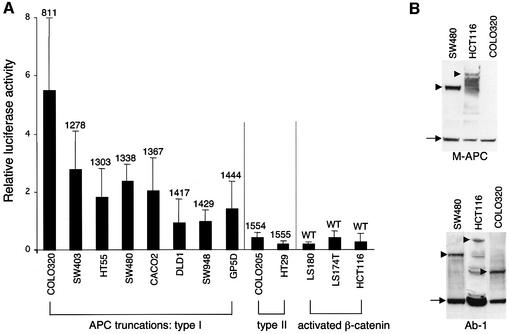
Fig. 4. Comparative TOPFLASH assays in colorectal cancer cell lines. (A) TCF-mediated transcription in colorectal cancer cell lines expressing wild-type or truncated APC, as indicated (codons of truncations are given above the bars); given are relative luciferase:Renilla values averaged from 3–6 independent experiments (error bars mark SDs; the Renilla values were obtained with pRL-CMV as an internal control, but essentially the same comparative values were obtained with pRL-TK and pRL-SV40). The TOPFLASH values are significantly lower in cell lines with activated β-catenin/wild-type APC or with APC type II truncations (retaining NES1506) compared with those with APC type I truncations (lacking NES1506). (B) Western blots of total cell extracts, probed with anti-M-APC (top) or with Ab-1 (bottom), to reveal full-length APC or APC truncations (arrowheads), and tubulin (arrows) as internal control. The short APC truncation in COLO320 cells is only detectable by Ab-1 (raised against an N-terminal peptide) but not by anti-M-APC (raised against the central third of APC). The levels of APC truncations in colorectal cancer cells are similar to one another, but appear to be generally higher than those of wild-type APC (though full-length APC is prone to degradation; see also Figure 5).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.