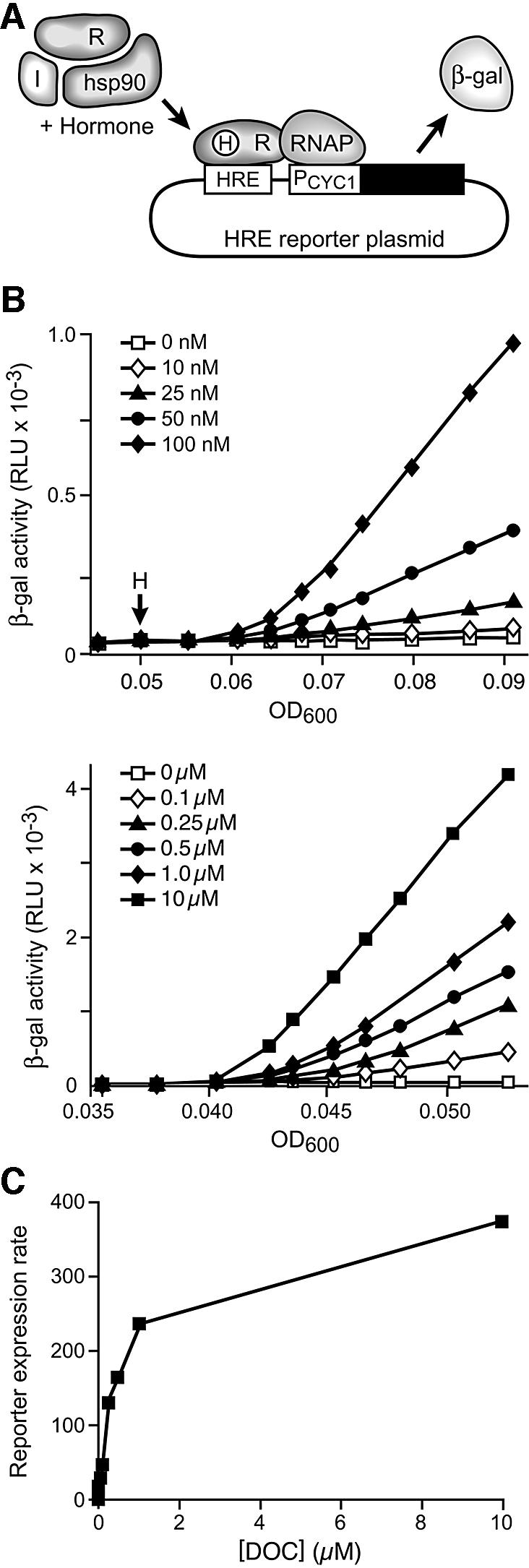
Fig. 1. Measurement of hormone-induced reporter activity. (A) Yeast strains were transformed with a hormone receptor expression plasmid, an immunophilin expression plasmid and a plasmid carrying a corresponding reporter gene. The receptor and immunophilin genes are transcribed from the strong constitutive glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase promoter. The reporter plasmid contains the lacZ gene transcribed from a truncated yeast cytochrome C1 promoter (PCYC1) downstream of receptor-specific hormone response elements (HRE). Receptor complexes, which contain yeast Hsp90 and other chaperones plus an immunophilin, are activated by hormone binding. The active receptor binds to HRE and recruits RNA polymerase complex (RNAP) to drive transcription from the reporter plasmid. (B) β-galactosidase was induced in the GR reporter strain by addition of deoxycorticosterone (H) at the concentrations indicated. β-galactosidase activities, measured in chemiluminescent relative light units (RLU), are plotted as a function of OD600. (C) To generate a DOC dose–response curve for the reporter gene expression rate, the slope (ΔRLU/ΔOD600) was calculated for the linear portion of each induction curve in (B) and plotted relative to hormone concentration.
