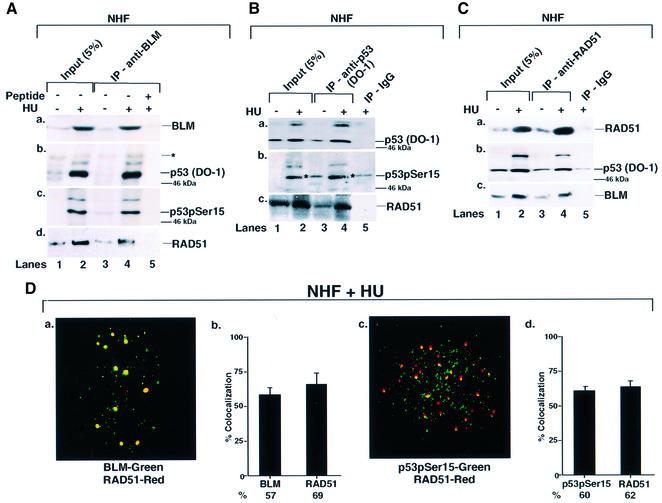
Fig. 2. BLM, p53 and RAD51 physically interact and co-localize in NHF. (A) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of BLM revealed p53 and RAD51. NHF was either left asynchronous (lane 1) or contact inhibited and treated with HU (lane 2) for 16 h. Lysates (400 µg) were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against BLM (C-18) in the absence (lanes 3 and 4) or presence (lane 5) of the peptide against which the anti-BLM antibody was raised. Input (lanes 1 and 2) indicates 5% of the lysate used for IP. The efficiency of IP was verified with self-antibody (a). Antibodies used for detection of other proteins in BLM IP were (b) anti-p53 (DO-1), (c) anti-phospho-p53 (Ser15) and (d) anti-RAD51 (Ab-1). Asterisks indicates a cross-reactive band. The position of the 46 kDa molecular weight marker is indicated. Lanes 1 and 3, minus HU; lanes 2, 4 and 5, plus HU. (B) IP of p53 revealed RAD51. The same as (A) except that the IP was carried out with antibodies either against p53 (DO-1) (lanes 3 and 4) or against the corresponding IgG (lane 5). Antibodies used for detection of other proteins in p53 IP were (b) anti-phospho-p53 (Ser15) and (c) anti-RAD51 (Ab-1). (C) IP of RAD51 revealed p53 and BLM. The same as (A) except that the IP was carried out with antibodies against RAD51 (Ab-1) (lanes 3 and 4) or against the corresponding IgG (lane 5). Antibodies used for detection of other proteins in RAD51 IP were (b) anti-p53 (DO-1) and (c) anti-BLM (C-18). (D) BLM, p53 and RAD51 co- localized. Contact-inhibited NHF were treated with HU for 16 h. Immunofluorescence was carried out with antibodies against (a) BLM (C-18)/RAD51 (Ab-1) and (b) phospho-p53 (Ser15) 16G8/RAD51 (Ab-1). Quantitation of (a) and (c) is represented in (b) and (d).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.