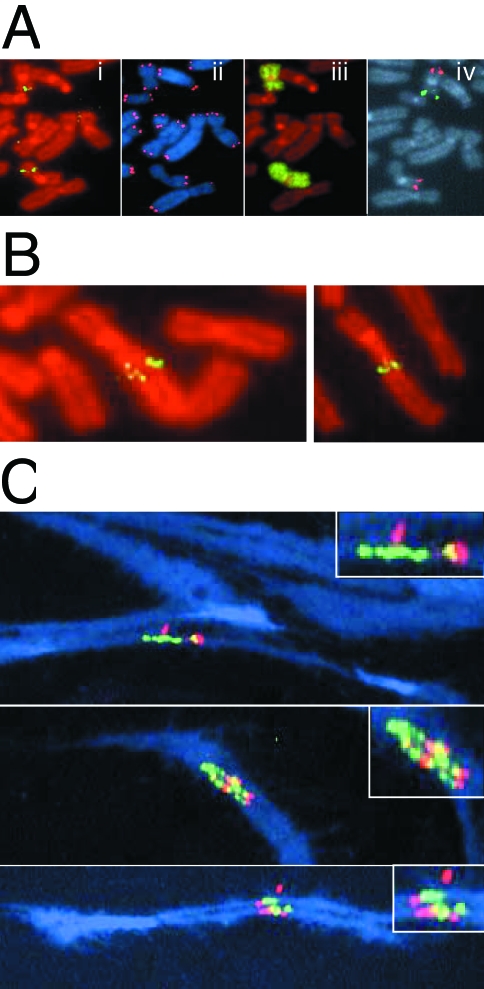
Figure 4.
Gene amplification resulting from the spontaneous telomere loss. (A) Metaphase chromosomes from subclone G71 hybridized with (i) a subtelomeric cosmid probe RT99 and counterstained with propidium iodide; (ii) a telomere-specific PNA probe and counterstained with DAPI; (iii) a chromosome 16-specific painting probe and counterstained with propidium iodide; and (iv) both a chromosome 16q-specific BAC clone GS-240-G10 (red) and a chromosome 16p-specific BAC clone GS-121-I4 (green). The marker chromosome is identified by the absence of hybridization with the GS-121-I4 BAC clone due to the terminal deletion associated with integration of the pNCT-tel plasmid. (B) Two additional metaphase chromosomes of subclone G71 demonstrating increased hybridization with the subtelomeric cosmid probe RT99 and variability in the size of the fragment joined onto the end of the marker chromosome. (C) Three metaphase spreads containing stretched chromosomes were hybridized with fluorescein-labeled cosmid RT99 (green) located immediately adjacent to the telomere and rhodamine-labeled cosmid 317H7 (red) located 1 Mb from the telomere. Overlapping RT99 and 317H7 hybridization signals appear yellow. Chromosomes were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The inserts are magnified views of the amplified regions.