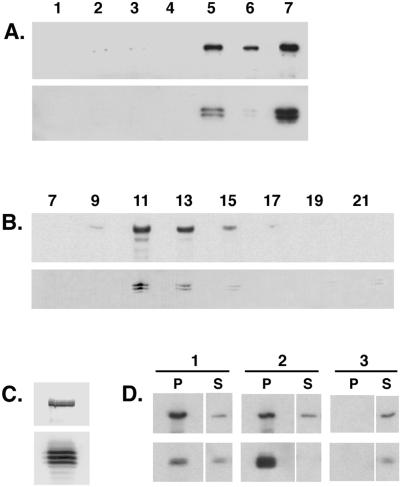
Figure 1.
The Drosophila cytoplasmic dynein IC associates with the dynein heavy chain. (A) The dynein IC is enriched in a standard preparation of MAPs from Drosophila embryos. Equal total protein from each step in the purification was analyzed by Western blotting with the use of an antibody that recognizes the cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain (upper panel) and an antibody that recognizes the dynein IC (lower panel). Lane 1, homogenate; lane 2, low-speed supernatant (57,000 × g); lane 3, high-speed supernatant (125,000 × g); lane 4, microtubule-depleted supernatant; lane 5, microtubule pellet; lane 6, Mg-ATP–extracted microtubule pellet; lane 7, Mg-ATP supernatant. (B) Embryo ATP MAPs were fractionated over a 5–20% sucrose density gradient and collected into 23 aliquots. Equal volumes of alternate fractions were analyzed by Western blotting. Upper panel, anti-dynein heavy chain; lower panel, anti-dynein IC. Fraction numbers are indicated above the appropriate lanes. Sedimentation standards were as follows: 19S, fraction 11; 11S, fraction 17; 2S, fraction 22. (C) The 19S dynein peak fraction from the sucrose gradient shown in B. The IC can be resolved as a triplet of polypeptides by one-dimensional PAGE. Upper panel, anti-dynein heavy chain; lower panel, anti-dynein IC. (D) Antibodies against the dynein heavy chain immunoprecipitate the dynein IC (column 1, P). Similarly, antibodies against the dynein IC immunoprecipitate the dynein heavy chain (column 2, P). No heavy chain or IC polypeptide is precipitated when beads alone are used (column 3). P, pellet; S, supernatant.