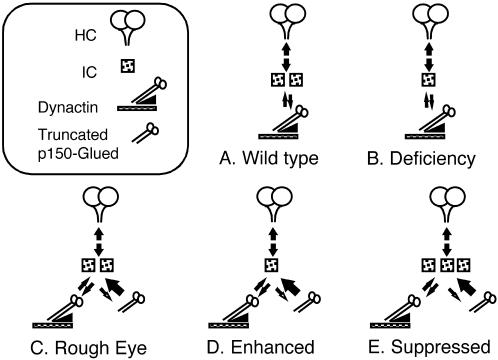
Figure 6.
Model for the in vivo interaction between the dynein IC and Glued1. A cartoon showing a model for the dosage-sensitive effect of the dynein IC on the rough-eye phenotype of Glued1. (A) In the wild type, the dynein IC associates with the heavy chain subunit and mediates the interaction with the p150-Glued subunit of dynactin. (B) In the presence of a deficiency that removes one copy of the dynein IC gene, the level of dynein IC is reduced, but it is still present at a level sufficient to support the interaction with dynactin, and no phenotype is detected. (C) In the case of Glued1, association of the truncated p150-Glued subunit with the dynein IC is favored. The truncated Glued polypeptide binds to the dynein IC but is unable to assemble into the dynactin complex or associate with cargo. Because of a limited pool of the IC subunit, the level of dynein capable of transporting cargo is reduced below a threshold, resulting in a rough-eye phenotype. (D) In the presence of the Glued mutation, when the level of dynein IC is reduced by a deficiency, the level of dynein-mediated transport is further reduced, and the rough-eye phenotype is enhanced. (E) With the addition of a dynein IC transgene, the level of dynein able to associate with cargo is increased, and the rough-eye phenotype is suppressed.