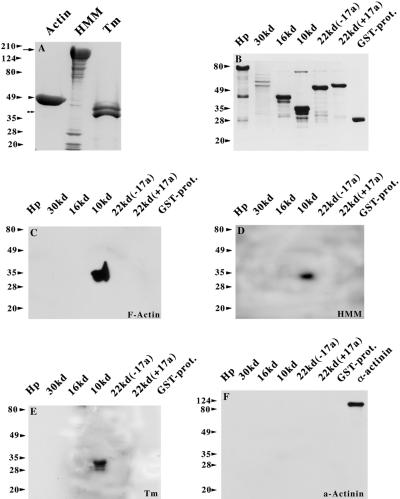
Figure 8.
Blot overlay assays of the 4.1R domains and the sarcomeric proteins F-actin, HMM, and tropomyosin (Tm). (A) Aliquots of 10 μg of purified skeletal muscle F-actin, HMM, and tropomyosin are shown by Coomassie blue staining. (B) Equivalent amounts of GST-4.1R fusion peptides and GST protein alone were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue as well. The GST-Hp fusion protein migrates as an ∼80-kDa protein instead of ∼55 kDa, which is presumably the result of posttranslational modifications that take place in the bacterial expression system. Furthermore, the 30-kDa domain is highly insoluble; thus, only limited amounts could be obtained. Some smaller bands that are detected in GST-Hp, GST-16 kDa, and GST-10 kDa are presumably the results of degradation. Three blots identical to the one shown in B were overlaid with native F-actin (C), HMM (D), and tropomyosin (E) and subsequently probed with anti-actin JLA20 mAb (C), anti-myosin MF20 mAb (D), and anti-tropomyosin CH1 mAb (E). In a control experiment, a similar blot was overlaid with the Z-disk protein α-actinin and subsequently probed with an anti-α-actinin mAb. In the last lane of the same blot, 10 ng of purified protein was loaded and served as positive control to the immunodetection system used. An ∼100-kDa band was detected that corresponds to α-actinin.