Figure 1.
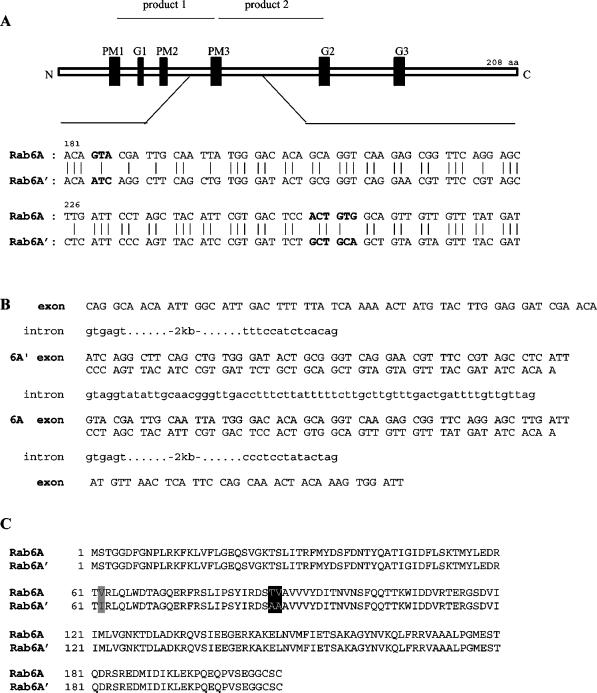
Rab6A gene organization reveals the presence of a duplicated exon. (A) Alignment of the divergent sequence stretch between human Rab6A and Rab6A′ cDNA sequences. Product 1 and product 2 represent partial sequences that were amplified by RT-PCR with degenerate Rab-specific primers on RNA from Caco-2 cells and HUVECs, respectively. Product 2 was used as a probe to isolate the corresponding Rab6A′ cDNA sequence from a human endothelial cell cDNA library. The 5′ and 3′ UTRs of both sequences are identical. Consensus domains for phosphate/magnesium binding (PM1–PM3) and guanine nucleotide binding (G1–G3) are depicted as black boxes. Nucleotide triplets that lead to amino acid divergence are in bold. (B) Partial genomic organization of the Rab6A gene reveals a duplicated exon separated by an intron of 66 bp. The exon for Rab6A′ sequence precedes the exon for Rab6A. (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of the Rab6A isoforms. Nonconservative amino acid changes are boxed in black, and conservative substitutions are boxed in gray.