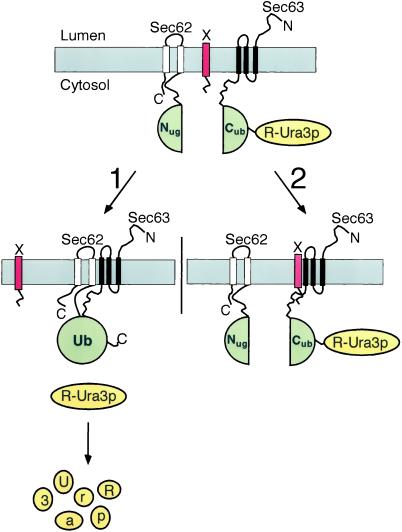
Figure 1.
Using the split-Ub technique to identify the binding sites of Sec62p for the Sec-complex by an in vivo competition assay. Nug-Sec62p, Sec63-Cub-RUra3p, and a fragment of Sec62p (X, red bar) are expressed in one cell. Pathway 1: when X does not or only weakly interacts with Sec63p, the Nug-labeled Sec62p is allowed to bind to the Cub-labeled Sec63p (both Ub-halves are in green). The induced proximity between Nug and Cub leads to their efficient reassociation. The assembled Ub is recognized by the UBPs, and the RUra3p reporter (yellow) is cleaved and subsequently degraded. The cells are phenotypically ura−. Pathway 2: X binds to Sec63p and displaces Nug-Sec62p from its complex. The increased distance between the Nug and Cub inhibits their reassociation. The RUra3p reporter remains linked to Cub and is not degraded. The cells are phenotypically ura+.