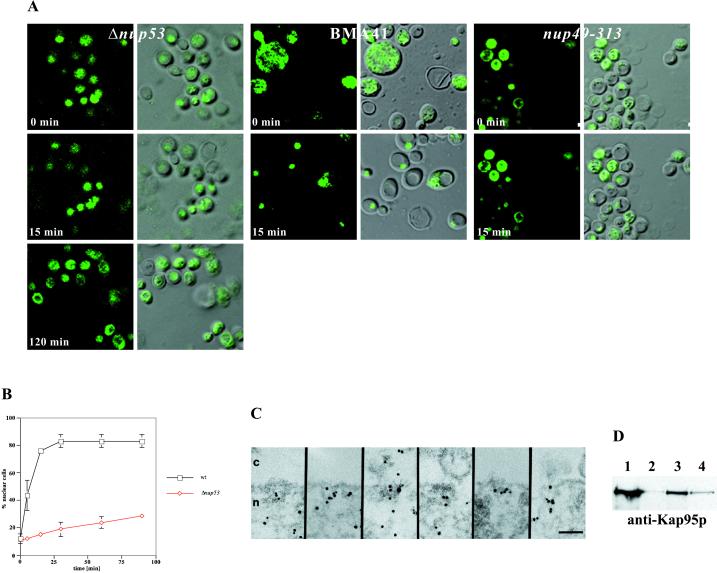
Figure 4.
Nup53p mediates nuclear import of a NLS-GFP reporter. (A) Intracellular localization of the NLS-GFP reporter in Δnup53, wild-type BMA41 control cells, and nup49-313 control cells (Table 1) after azide and deoxyglucose treatment (i.e., 0 min) and after recovery from the drug treatment in a glucose-containing medium (i.e., 15 and 120 min). Shown are confocal fluorescence micrographs (left) and coincident fluorescence/differential interference contrast images (right). (B) Quantification of the relative import rates in the Δnup53 and the wild-type BMA41 control cells by counting cells harboring nuclear fluorescence as a function of time. (C) Immunogold-EM reveals that the NLS-GFP reporter accumulates within the nuclear basket of the yeast NPCs in the Δnup53 cells (for quantification see Table 2). (D) Nup53p specifically interacts with the yeast nuclear import receptor Kap95p. For this purpose, ProtA-TEV-Nup53p was affinity purified by IgG-Sepharose chromatography and analyzed for copurifying components. Shown is a Western blot analysis with a polyclonal anti-Ka95p antibody revealing the specific interaction of Nup53p with Kap95p. Lane 1, NPC-containing fraction of a wild-type control strain (BMA41); lane 2, eluate derived from the wild-type control strain; lane 3, NPC-containing fraction of the strain expressing ProtA-TEV-Nup53p; and lane 4, eluate derived from the ProtA-TEV-Nup53p. Scale bar, 100 nm (C).