Figure 2.
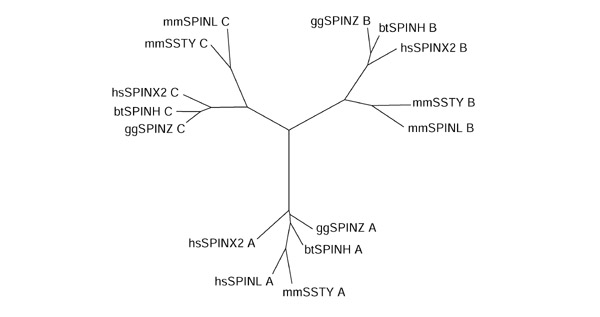
Phylogenetic tree of Spin/Ssty repeats. The tree was built from 15 repeats of five sequences. The labels stand for the repeats in the five proteins and consist of three fields: a two-letter code for the organism, an identifier for the protein sequence and the repeat subtype (see Figure 1 for terminology). Note the three groups of repeats: the amino-terminal repeats form one subtree, the central repeats form a second, and the carboxy-terminal repeats form a third. Thus, the phylogenetic classification of repeats matches the classification of the repeats by their positions in the proteins.
