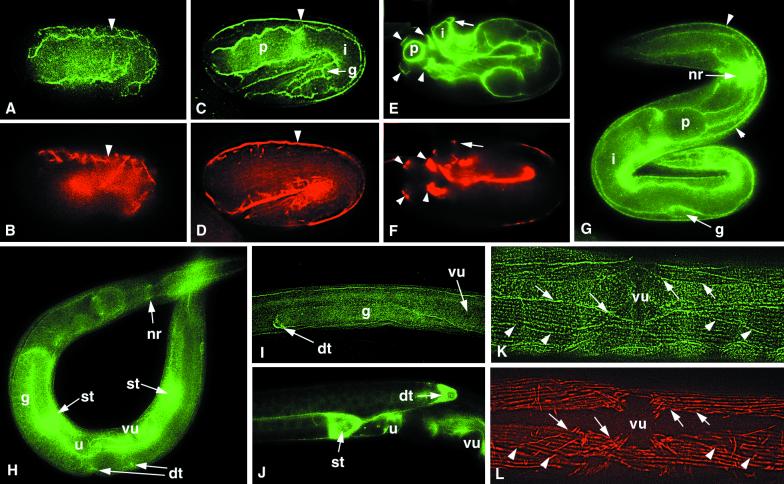
Figure 4.
Localization of NID-1 in wild-type animals. Animals were stained with anti–NID-1 (A, C, E, and G–K) and anti-myosin A (B, D, F, and L). (A and B) A comma stage embryo shows strong accumulation of NID-1 around body wall muscle cells (arrowhead) and diffuse association with the pharyngeal and intestinal primordia. (C and D) A twofold stage embryo shows NID-1 accumulation on the basal face of body wall muscles (arrowhead) and on the surfaces of the developing pharynx (p), intestine (i), and gonad (g). (E and F) A threefold stage embryo showing NID-1 localized under the four body wall muscle quadrants (arrowheads) and on the surfaces of the pharynx (p) and intestine (i). A body wall muscle quadrant over the intestine is indicated with an arrow. (G) In an L1 larva, strong NID-1 accumulation is seen around the nerve ring (nr). Staining is also seen at the basal face of body wall muscles (arrowheads) and on the surfaces of the pharynx (p), intestine (i), and gonad (g). (H) In an L4 larva, there is strong NID-1 accumulation on the developing spermathecae (st), vulva (vu), and uterus, and at the distal tip cells (dt). There is also weaker staining on the surfaces of the pharynx and intestine, at the nerve ring (nr), and under body wall muscles. (I) In a late L2-early L3 larva, NID-1 accumulates around the distal tip cell (dt) that is leading growth of the gonad (g). (J) An L4 larva showing strong NID-1 accumulation at the distal tip cell (dt), spermatheca (st), and uterus (u). (K and L) In an adult animal, NID-1 is distributed in a weak punctate pattern under the muscle cell dense bodies and is also present between the muscle quadrants. There is stronger NID-1 accumulation at the edges of the muscle quadrants (arrows) and weak accumulation between adjacent muscle cells (arrowheads). vu, vulva.