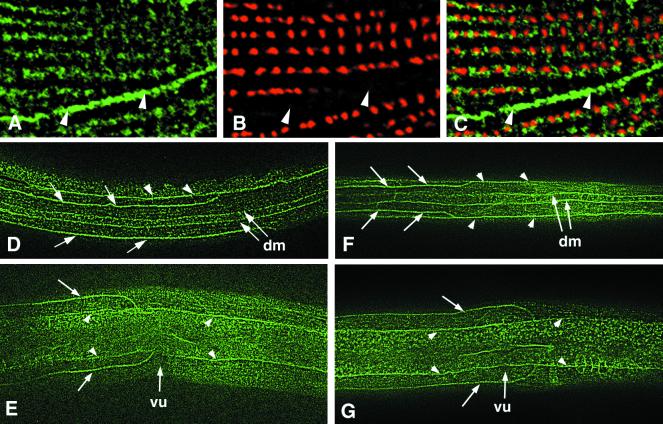
Figure 5.
NID-1 localization to sublateral nerves and muscle. Wild-type N2 (A–E) or nid-1(cg118) (F and G) animals were stained with anti–NID-1 (A, C–G) or anti–α-actinin (B and C) antibodies. (A–C) Part of a body wall muscle cell of an adult animal costained with anti–NID-1 and anti–α-actinin antibodies. (A) NID-1 accumulates beneath the dense body lines and along the interface between muscle cells (arrowheads). (B) The same region showing anti–α-actinin staining to visualize dense bodies. There is no α-actinin at the muscle cell interface. (C) The merged image of A and B shows that NID-1 localizes along a line that follows the dense bodies. (D and F) Dorsal views of L2 larvae; anterior is to the left. NID-1 is seen to accumulate on the left and right dorsal sublateral nerves (arrows), the dorsal edges of the left and right dorsal muscle quadrants (dm), and the lateral edges of the dorsal muscle quadrants (arrowheads). (E and G) Left lateral views of L4 larvae showing NID-1 accumulation on the dorsal and ventral sublateral nerves (arrows) and along the lateral edges of the dorsal and ventral body wall muscle quadrants (arrowheads). vu, vulvae.