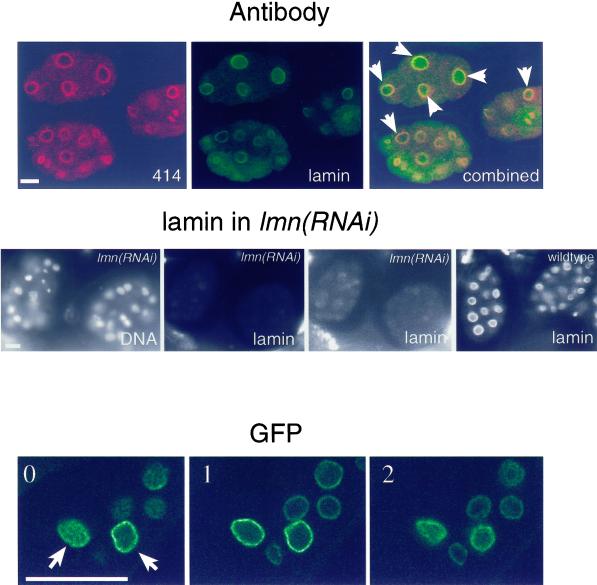
Figure 3.
Ce-lamin is present in the nuclear interior. Top panel: embryos were double stained with monoclonal antibody MAb414 (red) and affinity-purified Ce-lamin antibodies (green), and viewed with a confocal microscope. Overlap between Ce-lamin and nucleoporins appears in yellow. Most embryonic nuclei contained internal Ce-lamin, while MAb414 staining was confined to the nuclear envelope and the cytoplasm. Examples of nuclei with internal Ce-lamin staining are marked with arrows. Middle panel: DNA staining, left image; lamin staining, all other images. Both lmn-1(RNAi) images show the same confocal image of Ce-lamin staining, of the corresponding DNA-stained embryos. Intensity levels in the right lmn-1(RNAi) image were elevated, in order to detect residual lamin staining (as compared with the normal intensity levels in the left lmn-1(RNAi) image). Ce-lamin staining was eliminated in lmn-1(RNAi) embryos from both the nuclear envelope and the nuclear interior. The right image shows lamin staining in the control wild-type embryos. Bottom panel: three consecutive confocal sections, (one micron apart, 0 to 2), of adult tissue in the A12 line, which expresses low levels of Ce-lamin-GFP (see Figure 1B). Examples of nuclei with internal Ce-lamin-GFP staining are marked with arrows. Bar in each panel represents 10 μm and applies to all images in that panel.