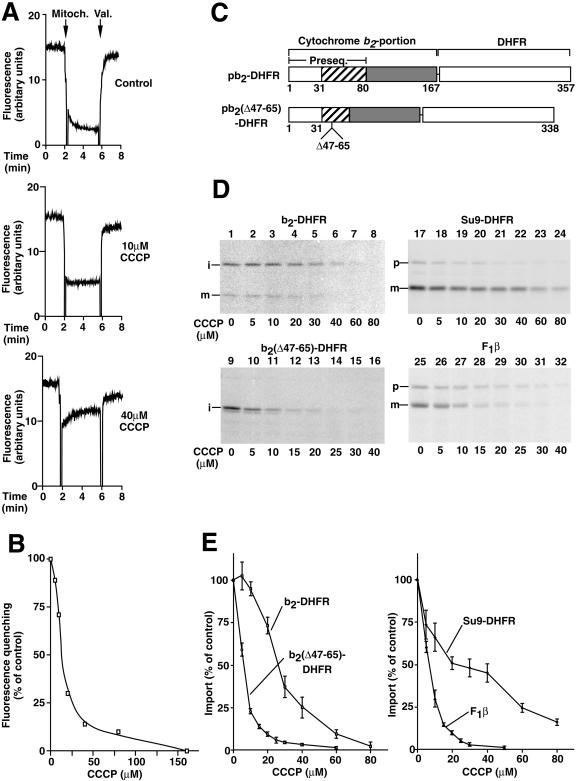
Figure 1.
The mitochondrial import of two b2-DHFR preproteins shows a differential dependence on the membrane potential Δψ. (A) The membrane potential ▵ψ of isolated yeast mitochondria was assessed at 25°C using the potential-sensitive dye DiSC3(5). CCCP was added as indicated. ▵ψ was assessed by the difference in fluorescence before and after the addition of valinomycin (Val.). (B) The fluorescence quenching at different concentrations of CCCP was quantified. The quenching in the absence of CCCP was set to 100%. (C) Cytochrome b2 hybrid proteins used in this experiment. pb2-DHFR consists of the first 167 amino acids of the cytochrome b2 precursor fused to the entire mouse DHFR by a linker of two amino acids. The bipartite cytochrome b2 presequence consists of an amino-terminal matrix-targeting sequence (residues 1–31) and a sorting sequence (residues 32–80). In pb2(▵47–65)-DHFR, residues 47–65 of pb2-DHFR have been deleted. (D and E) Isolated mitochondria were incubated with reticulocyte lysate containing 35S-labeled mitochondrial preproteins in the presence of the indicated concentrations of CCCP. After incubation for 5 min at 25°C, the import was stopped by the addition of 1 μM valinomycin. To remove nonimported preproteins, all samples were treated with proteinase K (final concentration, 40 μg/ml) for 15 min on ice. After reisolation and separation by SDS-PAGE, the amounts of imported proteins were quantified by phosphorimage analysis. The amount of protein imported in the absence of CCCP was set to 100% (control). Bars indicate the SEs of the means (from four to six independent experiments). p, precursor form; i, intermediate-sized form; m, mature form.