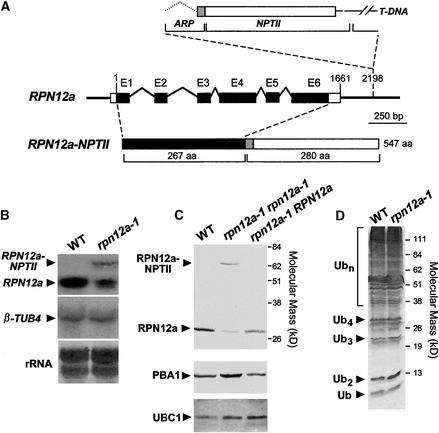
Figure 2.
Molecular and Biochemical Descriptions of the Arabidopsis rpn12a-1 Mutation.
(A) Scheme of the RPN12a gene and the predicted protein product of rpn12a-1, a RPN12a-NTPII translational fusion protein. Boxes and lines denote exons and predicted introns, respectively. Upon insertion of the T-DNA, the 3′ untranslated sequence of the RPN12a gene (bp 1661 to 2198) and the 5′ end of the ARP-NPTII gene from the T-DNA insertion form a chimeric intron that when spliced creates the translational fusion gene (RPN12a-NPTII) containing the full coding regions of RPN12a and the ARP-NPTII genes (Babiychuk et al., 1997). aa, amino acid.
(B) Detection of RPN12a transcripts in wild-type (WT) and rpn12a-1 seedlings by RNA gel blot analysis using a RPN12a gene probe. Arrowheads indicate the mRNA for wild-type RPN12a and the chimeric RPN12a-NPTII transcript. Equal amounts of total RNA were analyzed; loading was confirmed by staining for rRNA with methylene blue and by reprobing the blots with DNA encoding β-tubulin (β-TUB4).
(C) Immunoblot detection of the RPN12a protein. Total protein was extracted from wild-type seedlings and seedlings either hemizygous or homozygous for the rpn12a-1 mutation and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis with anti-RPN12a antibodies. Arrowheads indicate RPN12a and the RPN12a-NPTII fusion protein. Control immunoblot analysis was performed with antibodies against the CP β-subunit PBA1 and UBC1.
(D) Levels of ubiquitin (Ub) and ubiquitin–protein conjugates in wild-type and rpn12a-1 seedlings. Equal amounts of total protein were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis with anti-ubiquitin antibodies. The positions of the free ubiquitin, free multiubiquitin chains containing two to four monomers, and multiubiquitinated proteins are indicated.