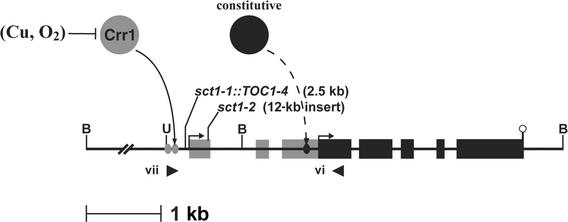
Figure 9.
Inserted Elements in CTH1 Prevent Normal Regulation of the Gene.
Putative copper-responsive promoter elements with the core sequence GTAC (gray ovals) in the 5′ flanking region of CTH1 stimulate initiation of the 3.1-kb transcript in –Cu or –O2 cells. Insertion of the 2.5-kb TOC1-4 element in sct1-1 strains between the transcription start site and the copper-responsive promoter elements disrupts transcriptional activation at the upstream initiation site, allowing constitutive expression of the 2.1-kb transcript from the downstream initiation site. sct1-2 strains contain a 12-kb insert in the first exon, preventing normal splicing of the 3.1-kb Cth1 mRNA and also blocking transcriptional interference between the –Cu/–O2 and +Cu transcription start sites. Candidate transcription initiation sites are indicated by arrows. Transcribed sequences exclusive to the 3.1-kb Cth1 mRNA are represented by gray rectangles, and black rectangles illustrate exons present in the 2.1-kb Cth1 transcript. An open circle designates the polyadenylation site. A Crr1-dependent activator is represented by a gray circle, whereas the black circle and the black oval denote a constitutive activator of transcription and a constitutive promoter, respectively. Arrowheads illustrate the primers used to amplify a 2.4-kb Cth1 PCR product, which provided the template for the probe used for DNA gel blot analysis (see Figure 7). B, BamHI; U, Sau3AI. Roman numerals indicate primers (see Table 1).