Figure 2.
Targeting to the Vacuole Blocks the Activity of CLV3.
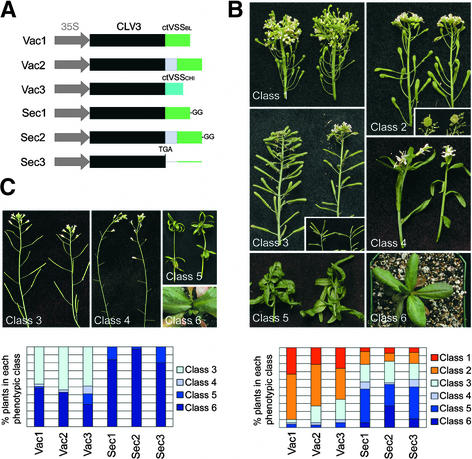
(A) Scheme of the fusion constructs. The C-terminal vacuolar sorting signal from barley lectin (ctVSSbl) was fused at the C terminus of CLV3 (Vac1) or CLV3 fused to a T7 peptide tag (Vac2). The ctVSS from tobacco chitinase A (ctVSSchi) was fused at the C terminus of CLV3 (Vac3). The ctVSSbl with two additional Gly residues (GG), which no longer functions as a vacuole-sorting signal, was attached either at the C terminus of CLV3 (Sec1) or CLV3-T7 (Sec2). Sec3 is obtained from Vac2 by deleting a single nucleotide that inserts a stop codon after the final amino acid of CLV3. All constructs are driven by the 35S promoter of Cauliflower mosaic virus.
(B) clv3-2 plants transformed with the constructs described in (A). Primary transformants were grouped into six phenotypic classes according to the severity of meristem termination. Class 1 plants showed no transgene activity and resembled clv3-2 mutants. Class 2 plants showed weak transgene activity and displayed the phenotype of weak clv3 alleles. (The inset shows the mass of cells accumulating in the SAM of these plants 10 weeks after transplanting.) Class 3 plants showed intermediate transgene activity that complemented the clv3 phenotype. These plants looked essentially like untransformed wild-type plants, although the SAMs terminated prematurely in some cases (inset). Most class 4 plants showed SAM termination before the production of floral organs, although some flowers formed and set seed. Class 5 and class 6 plants showed strong transgene activity, and all of the SAMs were terminated before producing flower organs (class 5) or inflorescence meristems (class 6). The graph at bottom shows for each construct the percentage of transformed plants that belong to each phenotypic class.
(C) Wild-type Columbia plants transformed with the constructs described in (A). Primary transformants were grouped into classes 3, 4, 5, and 6 as described in (B). The graph at bottom shows for each construct the percentage of transformed plants that belong to each phenotypic class.