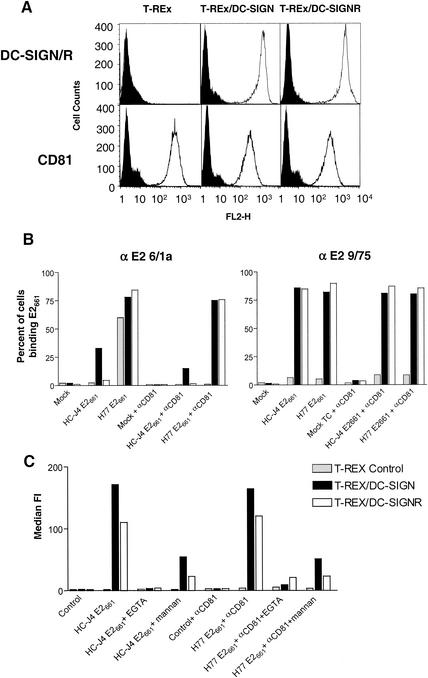
FIG. 2.
Binding of soluble E2 to cells expressing DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR. (A) Human 293-T and T-REx cell lines expressing DC-SIGN or DC-SIGNR (DC-SIGN/R) under an inducible promoter were incubated with 1 μg of doxycycline per ml to induce receptor expression. Parental T-REx cells, which do not express DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR, were also used. Expression of DC-SIGN, DC-SIGNR, and CD81 was monitored by FACS analysis with MAbs specific for DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR (m612) or anti-CD81 MAb 5A6 (open histograms). An isotype-matched mouse IgG was used as a negative control (solid shaded histograms). (B) Parental T-REx cells or cells expressing DC-SIGN or DC-SIGNR were incubated with the indicated E2 glycoprotein in the presence and absence of the anti-CD81 MAb 5A6. After washing, cell surface-bound E2 was detected with anti-E2 MAbs 6/1a and 9/75. MAb 6/1a can detect E2 when complexed with CD81, whereas the epitope recognized by MAb 9/75 is occluded when E2 binds CD81. The results are expressed as the percentage of cells binding E2 and are representative of two independent experiments. (C) Parental T-REx cells or cells expressing DC-SIGN or DC-SIGNR were incubated with the indicated E2 glycoprotein (H77 E661 binding was evaluated in the presence of anti-CD81 MAb 5A6) in the presence and absence of EGTA and mannan, and cell-bound E2 was detected with MAb 9/75. The results are expressed as the median fluorescence intensity (FI).