Figure 2.
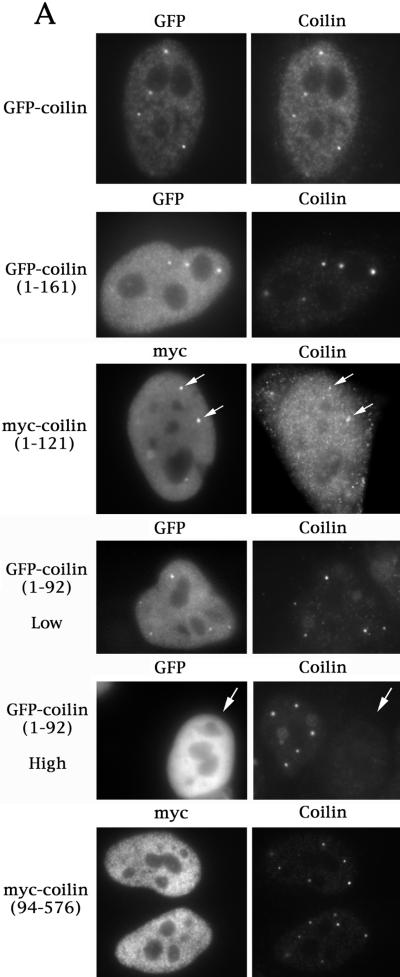
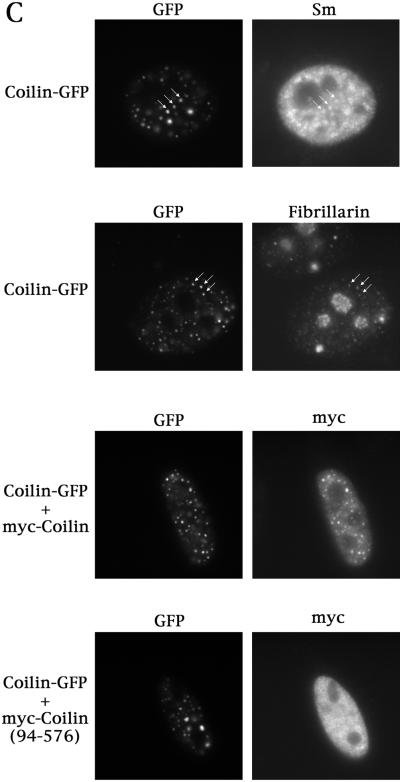
(A) The self-interaction domain of coilin is necessary and sufficient for CB localization. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated constructs were assayed for coilin localization by immunofluorescence using anticoilin antibody R508. The myc-coilin(1–121) and myc-coilin(94–576) constructs (Bohmann et al., 1995) were localized using antimyc antibodies. GFP-myc-NLS-coilin(1–92), labeled GFP-coilin(1–92), is shown at both high and low expression levels. The highly expressing GFP-myc-NLS-coilin(1–92) cell is indicated by an arrow. GFP-coilin(1–161) and myc-coilin(1–121) are shown at low expression levels. Facing page: (B) Overexpression of GFP-coilin disrupts CBs and results in the accumulation of GFP-coilin in thenucleolus. GFP-coilin was transfected into HeLa cells and immunofluorescence with coilin, SMN, and PML antibodies was conducted. (C) Fusion of GFP to the C-terminus of coilin apparently increases the number of CBs. Coilin was cloned into pEGFP-N3 (Clontech) and transfected into HeLa cells alone or in the presence of myc-coilin or myc-coilin (94–576). Immunofluorescence with antibodies to Sm (for snRNP localization), fibrillarin (for snoRNPs) or myc was conducted. Coilin-GFP localizes to numerous small foci which colocalize with Sm, fibrillarin, and ectopically expressed coilin, some of which are indicated by arrows. No colocalization was observed for coilin-GFP with myc-coilin(94–576).