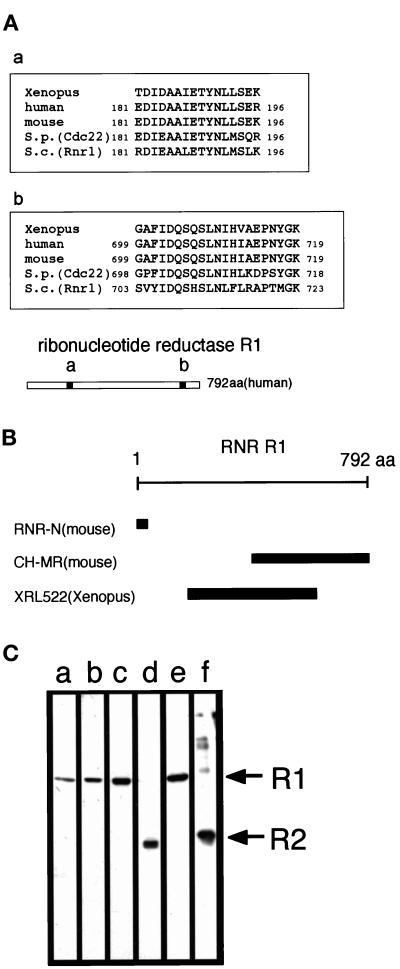
Figure 2.
Identification of an SPB activator as RNR R1. (A) Sequences of tryptic peptides from the isolated 85-kDa protein and their alignment with RNR R1 sequences from human, mouse, S. pombe (Cdc22), and S. cerevisiae (Rnr1) (EMBL accession no. X59543, K02927, X65116, and U18813, respectively) (a and b). The location of the corresponding peptides in the human R1 is shown (regions a and b in the bar). (B) Antigens used in the production of the anti-R1 polyclonal antibodies used in this study (See text for details). (C) Anti-R1 antibodies recognize the 85-kDa protein in Xenopus egg mitotic extracts. (lanes a–c) The 200K fraction of egg mitotic extracts was loaded on 10% SDS-PAGE, transferred onto nitrocellulosemembrane, and blotted with affinity-purified anti–RNR-N (a), anti–CH-MR (b), and anti-XRL522 (c) antibodies. (lanes d and f) The anti-R2 antibody (anti-MRSS) recognizes recombinant mouse R2 (f) and a 45-kDa polypeptide in the 200K fraction, a putative Xenopus homologue of RNR R2 (d). (lane e) The SPB activator purified from Xenopus egg mitotic extracts (fraction f from the second anion-exchange column, Figure 1A, lanes f) was probed with a mixture of anti-R1 (anti-XRL522) and anti-R2 (anti-MRSS) antibodies.