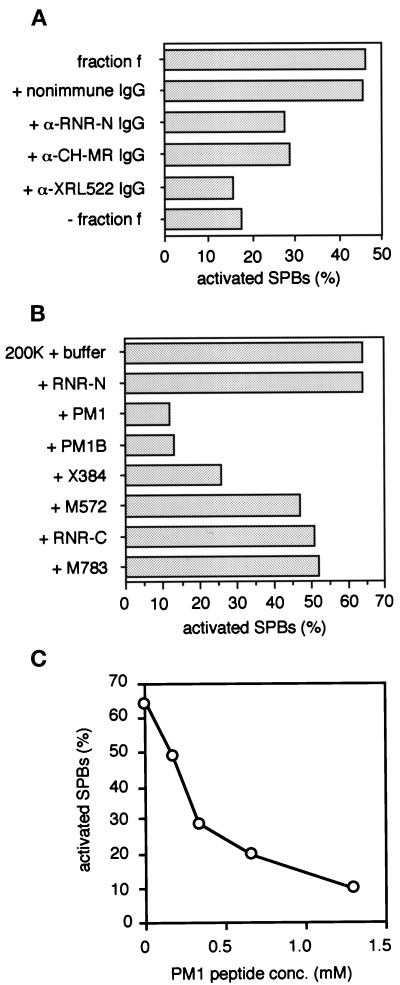
Figure 4.
Effects of Anti-R1 antibodies and R1 partial peptides on SPB activation. (A) Anti-R1 antibodies inhibit SPB activation. Affinity purified polyclonal antibodies against R1—anti–RNR-N, anti–CH-MR, and anti-XRL522—and nonimmune rabbit IgG were added separately to the SPB activator purified from Xenopus egg mitotic extracts (Figure 1A, lanes f) to a final concentration of 50–140 μg/ml, incubated on ice for 2 h, and then subjected to the SPB activation assay. Horizontal axis, the percentage of activated SPBs (N = 400). (B) Effects of R1 partial peptide addition to the 200K fraction of Xenopus egg mitotic extracts. The 200K fraction was mixed with each of the peptides, RNR-N, PM1, PM1B, X384, M572, RNR-C, or M783, at 1.2 mM final concentration andsubjected to the SPB activation assay. Horizontal axis, the percentage of activated SPBs (N = 300). (C) The PM1 peptide suppresses SPB activation by the 200K fraction in a concentration-dependent manner. The 200K fraction was mixed with the PM1 peptide at various concentrations (0.17–1.3 mM) and subjected to the SPB activation assay. Horizontal axis, the peptide concentration (mM); vertical axis, the percentage of activated SPBs (N = 100).