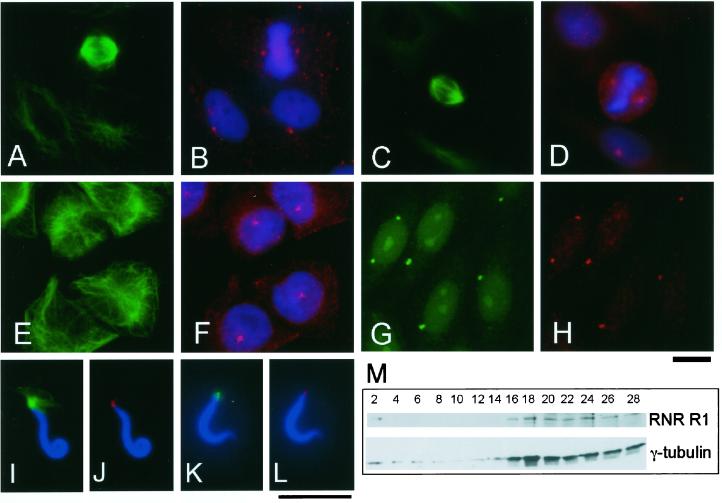
Figure 6.
R1 is a centrosomal component in animal cells. (A–F) R1 localizes to the centrosome in animal cells. Xenopus A6 (A and B) and CHO cells (C–F) were triple-stained with anti–α-tubulin (B-5-1-2; green in A, C, and E), DAPI (blue in B, D, and F), and anti-R1 antibodies: anti–CH-MR (red in B) or anti-XRL522 (red in D and F). (G and H) R1 is an integral component of the centrosome. CHO cells incubated with nocodazole for 4 h before fixation were double-stained with anti-pericentrin (green in G) and anti–RNR-N (red in H). Bar, 10 μm. (I–L) R1 localizes to the sperm centrosome. Demembranated Xenopus sperm heads were incubated in a Xenopus egg mitotic extract (HSE) containing Rd-tubulin (I and J) or in a control buffer (K and L). (I and J) The sperm heads were stained with anti-XRL522 (red in J) and DAPI (blue). In (I), a microtubule aster of Rd-tubulin is shown in green. (K and L) The sperm heads were stained with anti–α-tubulin (B-5-1-2; green in K), anti-XRL522 (red in L), and DAPI (blue). Bar, 10 μm. (M) Centrosomes isolated from CHO cells contain R1. The centrosomes from CHO cells were fractionated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation, and the resulting fractions were processed for immunoblot analysis with anti–γ-tubulin (GTU88) and anti-human R1 (KM1466) antibodies. R1 cosediments with the fractions that are recognized by the γ-tubulin antibody.