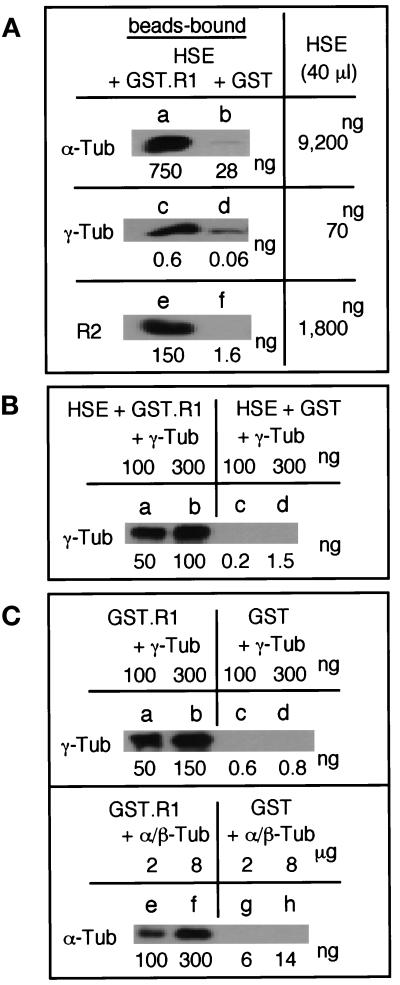
Figure 7.
R1 interacts with γ- and α/β-tubulin and R2 in vitro. (A) GST-R1 interacts with γ- and α-tubulin and R2 in Xenopus egg mitotic extracts. GST-R1 (37 μg; a, c, and e) or GST (33 μg; b, d, and f) was incubated with 40 μl of a Xenopus egg mitotic extract (HSE) and recovered with Glutathione-Sepharose beads. Total amounts of α- and γ-tubulin and R2 in the beads-bound fractions and HSE were determined by quantitative immunoblotting with anti–α-tubulin (B-5-1-2), anti–γ-tubulin (GTU88), and anti-R2 (anti-MRSS) antibodies using purified proteins as standards. (B) Exogenous γ-tubulin interacts with GST-R1 in Xenopus egg mitotic extracts. GST-R1 (a and b) or GST (c and d) was incubated with HSE containing 100 ng (a and c) or 300 ng (b and d) of S. pombe γ-tubulin and processed as in (A). (C) γ-Tubulin and α/β-tubulin directly bind to GST-R1. GST-R1 (a, b, e, and f) or GST (c, d, g, and h) was incubated with 100 ng (a and c) or 300 ng (b and d) of S. pombe γ-tubulin or with 2 μg (e and g) or 8 μg (f and h) of porcine α/β-tubulin and processed as in (A).